Figure 3.
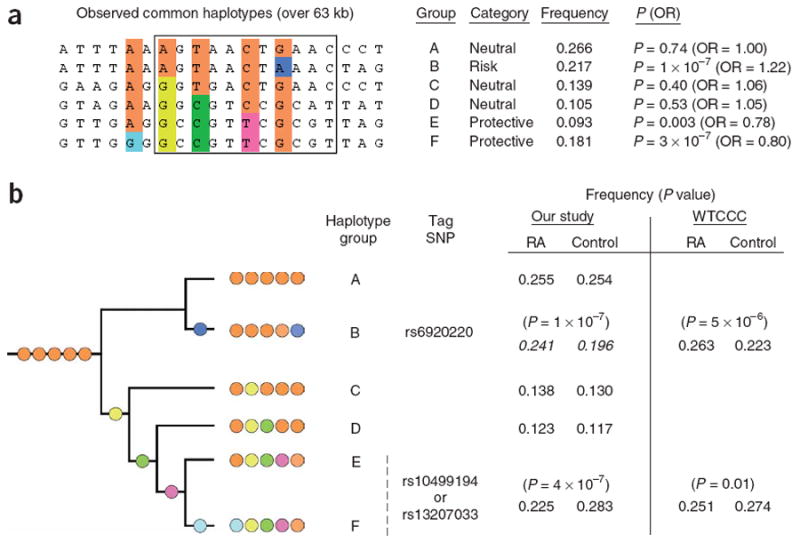
Haplotype analysis in our replication samples and in the WTCCC study of ∼2,000 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and ∼3,000 controls. Haplotype analysis with 17 genotyped SNPs and 3 imputed SNPs across a 63-kb region of strong LD in our replication samples (2,283 unrelated CCP+ rheumatoid arthritis cases and 3,258 unrelated controls) yielded six haplotypes with population frequency >5% (constituting 96% of all observed haplotypes). When expressed relative to the minor allele, two haplotypes tagged by rs10499194 are ‘protective’ (haplotypes E and F) and a single haplotype tagged by rs6920220 provides ‘risk’ (haplotype B). (a) The haplotype group, risk category and frequency of all samples are shown. The P value (P) and odds ratio (OR) for each haplotype were calculated by comparing each haplotype to all others, using the statistical program WHAP28. The highlighted SNPs (in order: rs1878658, rs675520, rs9376293, rs10499194, rs6920220 (imputed)) define the six common haplotypes. The 11 SNPs within the box were used to define haplotype phylogeny in b. (b) Five SNPs served to uniquely identify the phylogeny of the six common haplotypes. Haplotype frequencies (cases and controls) and P values from single-marker analysis in our replication samples or from the WTCCC study (where rs13207033 is the WTCCC SNP) are shown.
