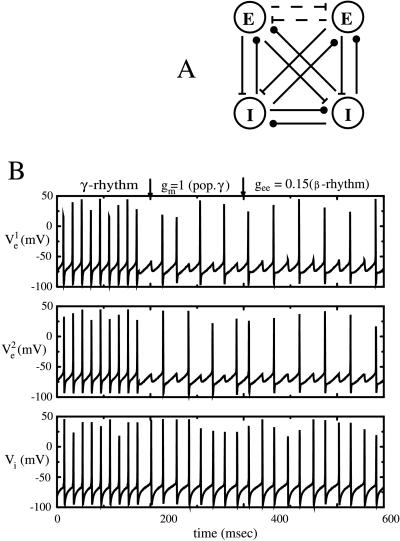
Figure 2.
(A) Minimal network for investigating local synchronization of gamma and beta rhythms. For the gamma rhythms, the E-E connections are absent; for the beta rhythms, they are a necessary part of the circuit. (B) Gamma-to-beta transition of local rhythms occurs as the AHP is turned on and the local E-E connections are strengthened. Parameters are as in the Appendix. For the gamma rhythm, gee = 0 and gm = 0. At the first arrow, gm is set to 1, switching the rhythm from gamma to a rhythm in which the E-cells miss beats and fires nonsynchronously. At t = 400, gee = 0.15, and the network quickly suppresses the nonsynchronous solution, leaving only the synchronous local state. Throughout the transitions, the I cells shown below exhibit only minor changes, slowing down slightly because of the decreased excitation (excitation every other cycle).