Figure 1.
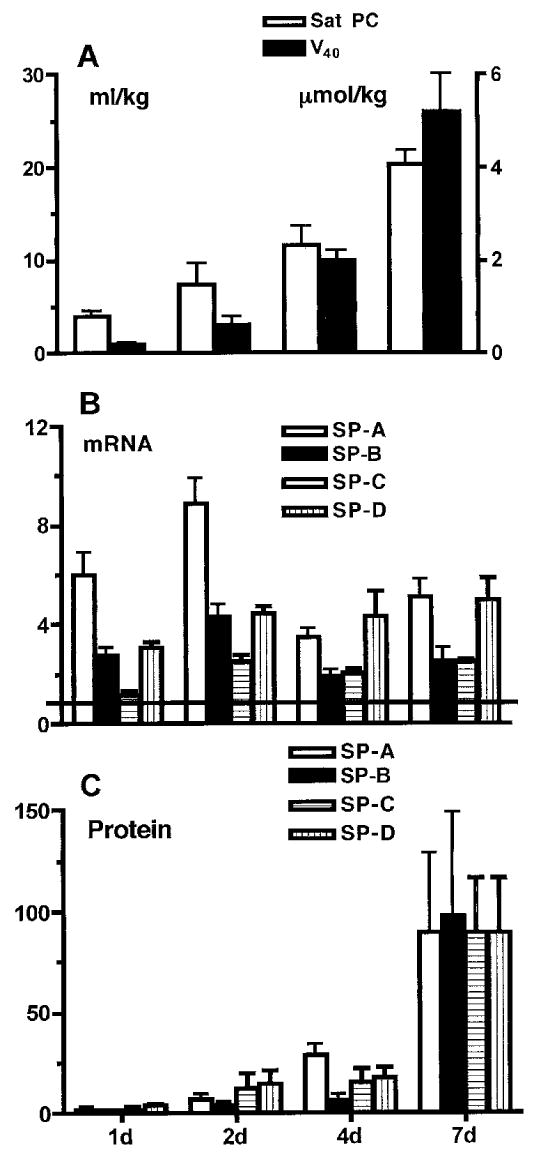
Surfactant proteins (SP) and lipids increase as lung function improves following intra-amniotic endotoxin. Fetal sheep were exposed to 20 mg E. coli endotoxin given by intra-amniotic injection at the intervals given on the horizontal axis prior to preterm delivery at 125 d gestation. (A) Lung gas volume (V40; solid bars) measured as mL/kg air at 40 cm pressure increased over 7 d, as did the amount of saturated phosphatidylcholine (Sat PC, μmol/kg; hollow bars). (B) The amount of mRNA for the surfactant proteins in lung tissue also increased and remained elevated relative to the normalised values of 1 for lung tissue from lambs not exposed to endotoxin. (C) The amounts of the surfactant proteins in bronchoalveolar lavage increased from the normalised value of 1 for lambs not exposed to intra-amniotic endotoxin. Data calculated and redrawn from Ref. 24. (B) and (C): hollow bars, SP-A; solid bars, SP-B; hatched bars, SP-C; stippled bars, SP-D.
