Figure 5.
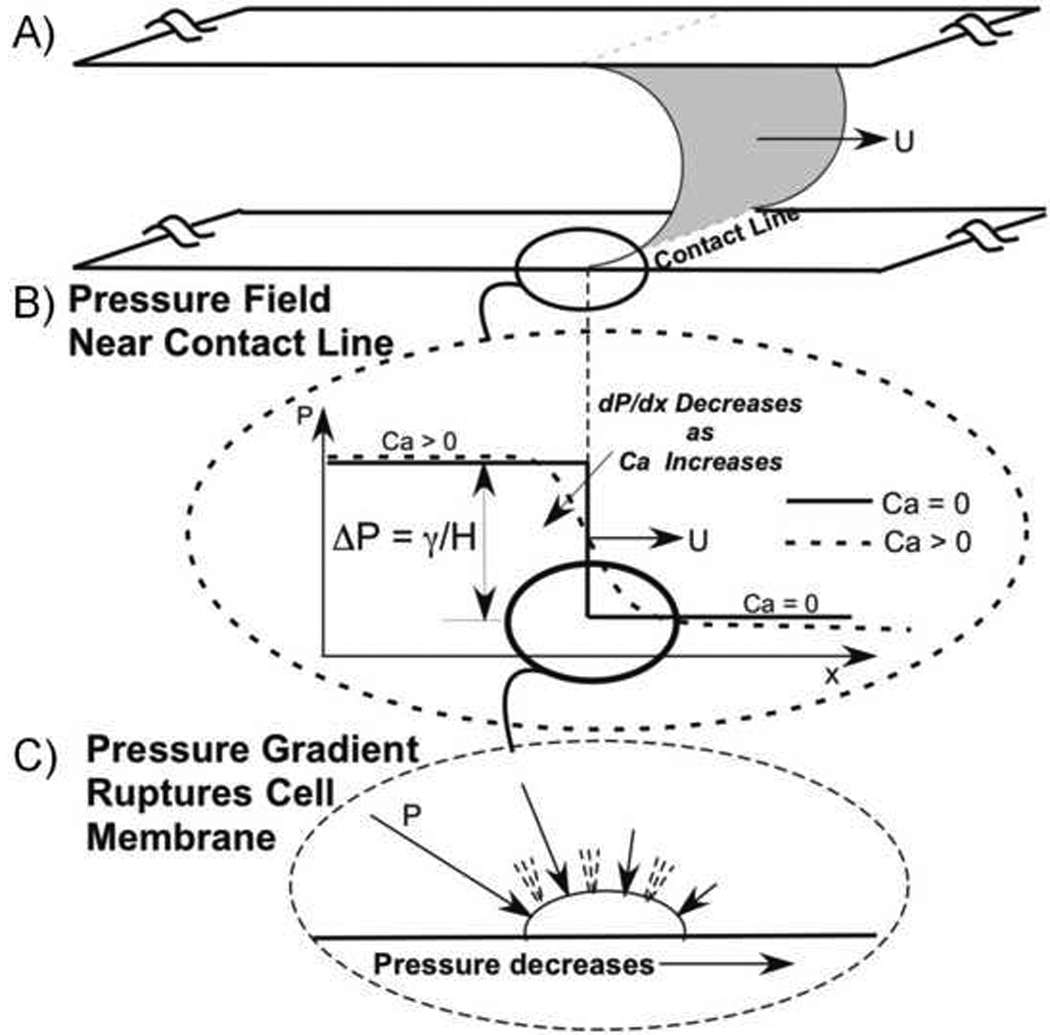
A: Schematic of an air-liquid interface propagating between two flat plates at velocity U with a uniform contact line on the top/bottom wall. B: Pressure field near the interface for zero and nonzero capillary number (Ca). The spatial gradient in pressure, dP/dx, increases with decreasing Ca. C: Spatial gradients in pressure result in a fore-aft pressure difference across the epithelial cells and this pressure difference is hypothesized to rupture the membrane and lead to necrosis.
