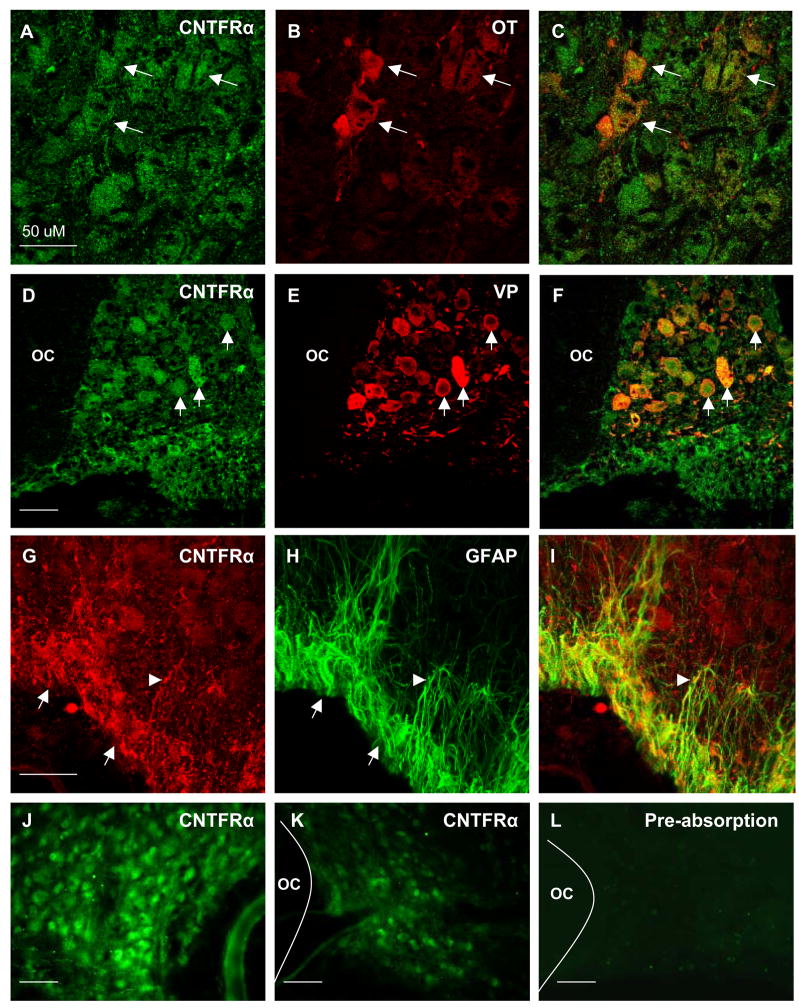
Figure 1.
CNTFR-ir was observed in magnocellular neurons and astrocytes throughout the SON. (A–C) Dual fluorescent colocalization of anti-CNTFRα (A), with anti-oxytocin (B), revealed extensive colocalization in oxytocin-ir neurons (C, arrows). Likewise, dual fluorescent colocalization of anti-CNTFRα (D), with anti-vasopressin (E), revealed complete colocalization in all vasopressinergic neuron soma (F, arrows). In addition, CNTFRα-ir (G, arrows) was prevalent in GFAP-ir astrocyte cell bodies within the VGL (H). Close examination revealed CNTFRα-ir astrocyte cell processes originating from the VGL extending into the magnocellular region of the SON (arrowheads). As shown in panels J and K, the observed differences in mRNA levels (see Figure 2) are also reflected in the relative level of immunoreactivity observed when comparing the contralateral intact sprouting SON (J) to the lesioned SON (K) of the same animal at 7 days post lesion. (L) Preabsorption controls revealed that a 10 fold excess of purified rat recombinant CNTFRα completely eliminated immunoreactivity. Negative omission controls revealed the same (not shown). OC = optic chiasm, Magnification bars = 50μM.