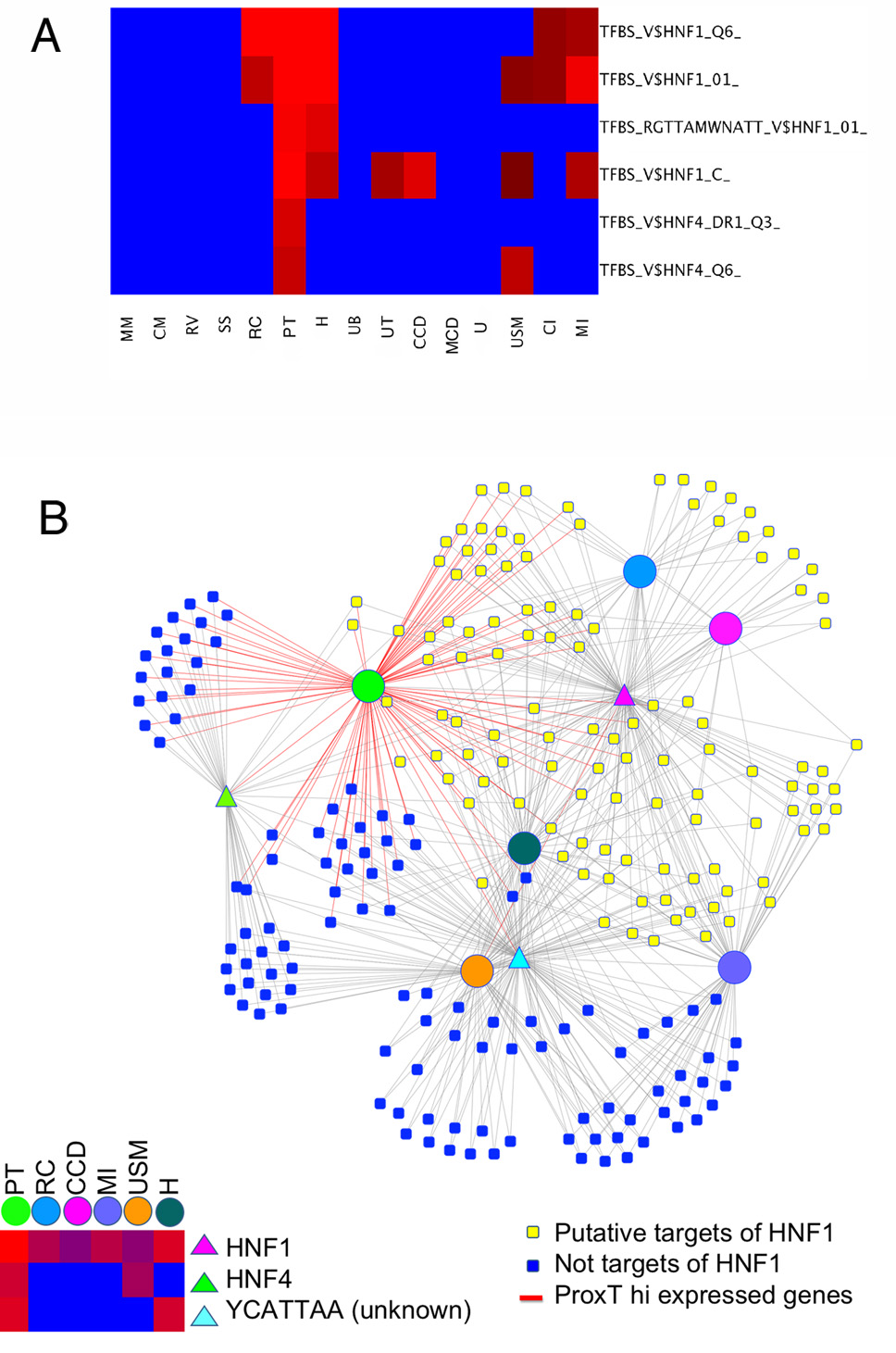
Fig. 6. Occurrence of transcription factor binding sites in promoters of highly expressed genes.
A. This heat map shows the very high frequency of HNF1 and HNF4α binding sites in the highly expressed genes of certain compartments. Red indicates high and blue shows low statistical significance. Four related defined binding sites were used for HNF1 and two for HNF4α. For example, P-values for V$HNF1_Q6_ were 10−4.9 for RC, 10−10 for PT, 10−6 for H, 10−2.3 for CI and 10−2.7 for MI, while not significant for any other compartment. This strongly suggests that HNF1 drives the expression sets of downstream target genes carrying promoter binding sites, in certain compartments. B. Diagram illustrating relationships of compartments (circles), transcription factors (triangles) and candidate target genes (squares). Lower left shows heat map of significance of binding sites in highly expressed genes in compartments, summing the data shown in panel A. Yellow squares are targets of HNF1, while blue are not. The overlapping set of targets expressed in multiple compartments is apparent. MM, E11.5 metanephric mesenchyme, CM, E15.5 cap mesenchyme, RV, E12.5 renal vesicle, S, E15.5 S-shaped body, RC E15.5 renal corpuscle (glomerulus), PT, E15.5 proximal tubules, H, E15.5 Loop of Henle and distal tubule, UB, E11.5 ureteric bud, UT, E15.5 tipregion of collecting ducts, CCD, E15.5 cortical collecting ducts, MCD, E15.5 medullary collecting duct, U, E15.5 urothelium, USM, E15.5 ureteral smooth muscle layer, CI, E15.5 cortical and nephrogenic interstitium (cortical stroma), MI, E15.5 medullary interstitium, (medullary stroma). YCATTAA is a conserved binding site for which the corresponding transcription factor is not yet known.