FIGURE 3. TNF-α induces recruitment of signaling adaptors and RhoA into lipid rafts.
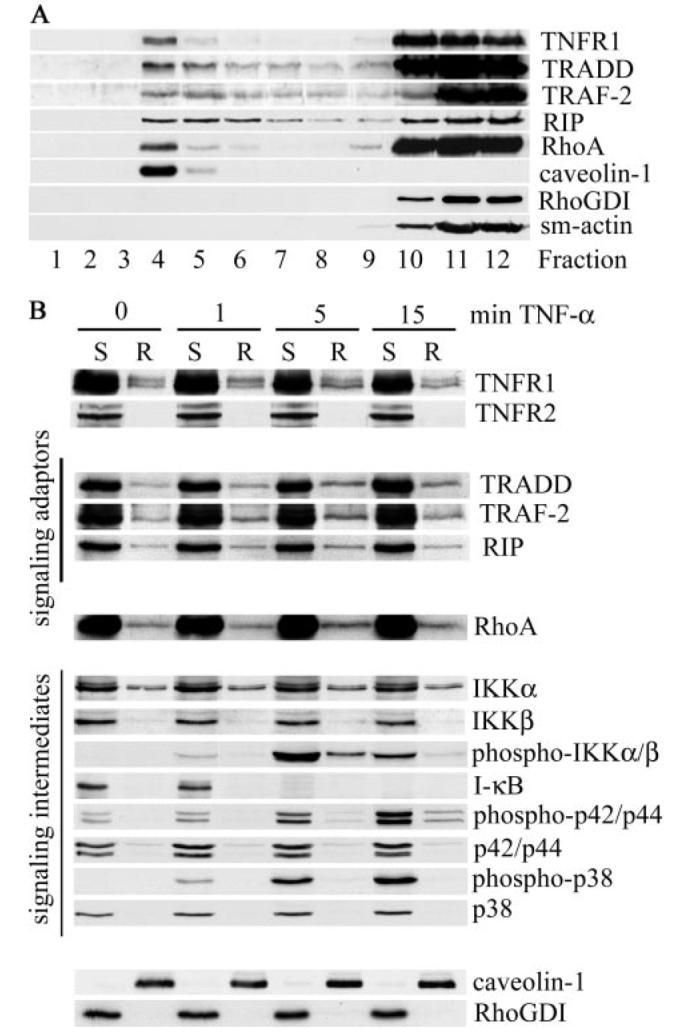
Human airway smooth muscle cells were extracted with cold Triton X-100 and fractionated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation (A) or stimulated with TNF-α for the indicated times (B) before isolation of Triton X-100-soluble (S) and Triton X-100-insoluble, octyl glucoside-soluble raft fractions (R). Equal volume samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed with specific antibodies for the expression of TNFR1, signaling adaptors, signaling intermediates, and RhoA as indicated. Lipid rafts were identified by the expression of the raft-resident protein, caveolin-1, whereas soluble fractions expressed RhoGDI. The cytoskeletal protein, smooth muscle actin (sm-actin), was restricted to soluble fractions.
