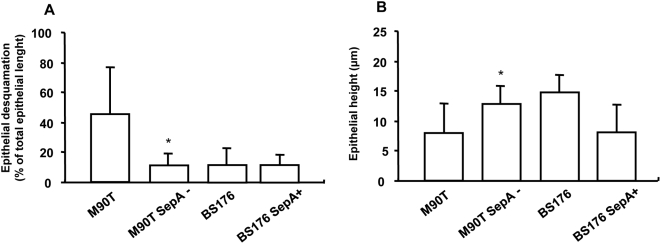
Figure 4. Role of SepA upon epithelial morphology in the human colon induced by S.flexneri.
Tissues were infected for 3 h with various strains of S.flexneri : invasive strain (M90T), non-invasive strain (BS176), invasive strain deleted for SepA (M90T SepA−), non-invasive strain expressing SepA (BS176 SepA+). (A) M90T SepA− induced a significant reduction in the epithelial desquamation as compared to M90T. However, BS176 SepA+ did not increase epithelial desquamation as compared to BS176. (B) M90T SepA− induced a significant increase in the height of the surface epithelium as compared to M90T and BS176 SepA+ reduced the epithelial height as compared to BS176. Data are expressed as mean±SEM (n = 10, * p<0.05 as compared to M90T).