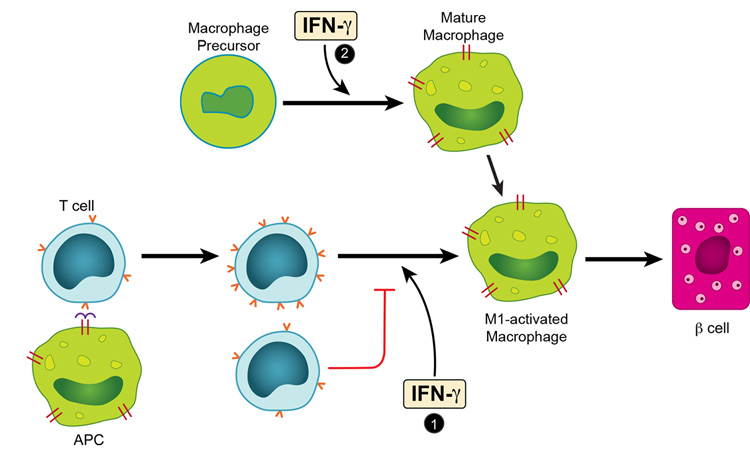
FIGURE 8.
IFN-γ effects in the induction of the inflammatory response and the consequent diabetes mediated by BDC T cells. As a result of the interaction between an APC containing a diabetogenic antigen and a diabetogenic CD4 T cells, two sets of activated CD4 T cells are generated, differing in the extent of expression of their TCR (noted by the numbers of “v” in red in the figure). In the islet tissue these cells generated an inflammatory exudate rich in M1-activated macrophages. IFN-γ, exerts an effect in this step, marked as # 1 allowing the TCR high T cell to predominate. In the absence or blocking of IFN-γ in the step 1, the TCR-low predominates and the resulting exudate has features of the M2-activated macrophages, and β-cell function is preserved. The macrophage precursor differentiates in a process influenced by IFN-γ, see # 2, to generate macrophages that respond to inflammatory cues.