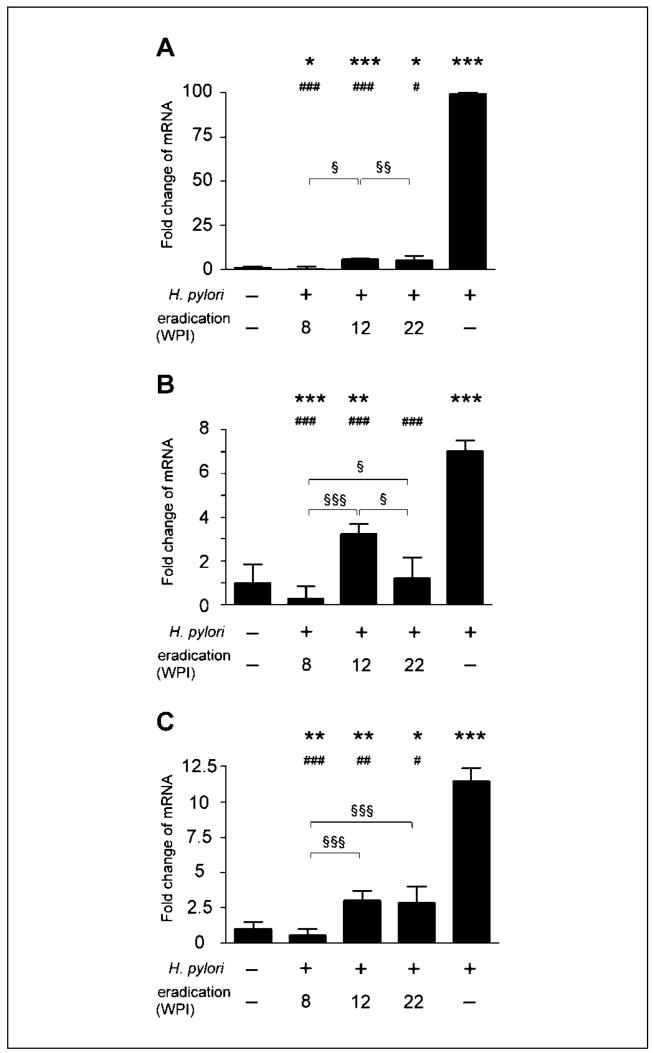
Figure 3.
Relative mRNA levels of IFN-γ (A), TNF-α (B), and iNOS(C) in the gastric tissue. Data are presented as fold change relative to uninfected INS-GAS mice. H. pylori–infected mice without eradication therapy had significantly higher levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and iNOS mRNA (P < 0.001). H. pylori eradication at 8 WPI had statistically lower IFN-γ, TNF-α, and iNOS mRNA levels compared with uninfected mice and infected mice without eradication therapy. H. pylori eradication at 12 or 22 WPI had IFN-γ, TNF-α, and iNOS mRNA levels that were significantly higher than those in uninfected mice but lower than those in infected control mice that did not receive eradication therapy. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001, compared with uninfected mice. #, P < 0.05; ##, P < 0.01; ###, P < 0.001, compared with infected mice that did not receive antimicrobial eradication. §, P < 0.05; §§, P < 0.01; §§§, P < 0.001, comparison as indicated.