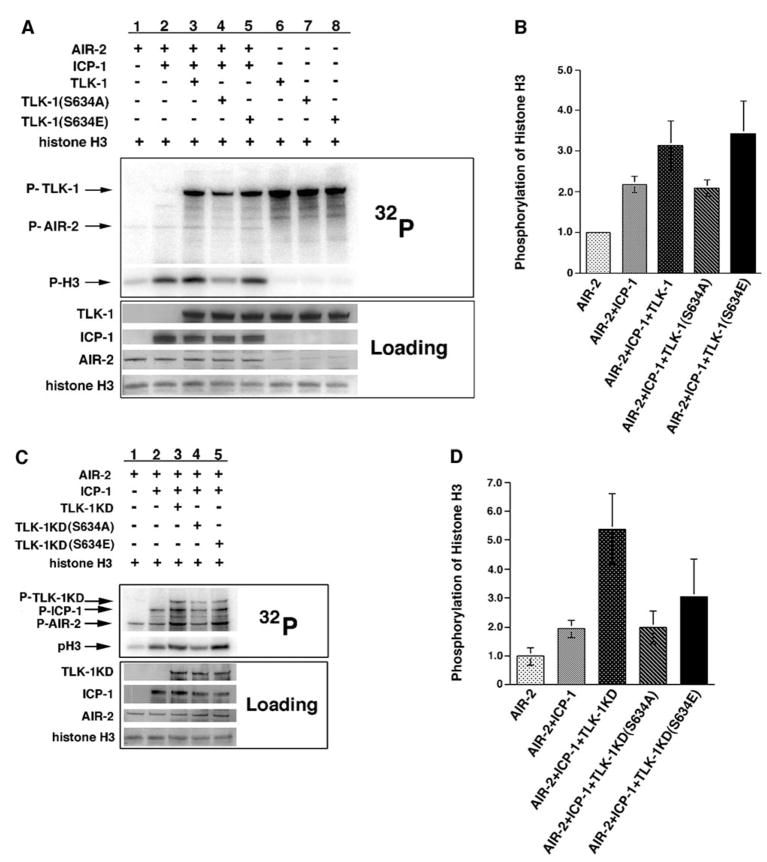
Figure 5. Phosphorylated TLK-1 Increases AIR-2 Kinase Activity.
(A) AIR-2 was incubated with histone H3 in the presence and absence of ICP-1 and wild-type TLK-1, TLK-1(S634A), and TLK-1(S634E) in kinase buffer supplemented with γ-32P-ATP. AIR-2 phosphorylation of histone H3 was increased in the presence of ICP-1 (lanes 1 and 2). A further increase in H3 phosphorylation occurred when wild-type TLK-1 or TLK-1(S634E) was incubated with AIR-2/ICP-1 (lanes 3 and 5). Histone H3 phosphorylation did not increase in the presence of TLK-1(S634A) (lane 4). Although all three TLK-1 fusion proteins underwent autophosphorylation, none of them phosphorylated histone H3 in the absence of AIR-2/ICP-1 (lanes 6–8).
(B) Quantitation of histone H3 phosphorylation in the kinase assays shown in (A). Error bars represent the standard deviation from at least three separate experiments.
(C) AIR-2 was incubated with histone H3 in the presence and absence of ICP-1 and kinase-dead versions of TLK-1, TLK-1(S634A), and TLK-1(S634E) in kinase buffer supplemented with γ-32P-ATP. AIR-2 phosphorylation of histone H3 was increased in the presence of ICP-1 (lanes 1 and 2). A further increase in H3 phosphorylation occurred when TLK-1KD or TLK-1KD(S634E) was incubated with AIR-2/ICP-1 (lanes 3 and 5). Histone H3 phosphorylation was not increased in the presence of TLK-1KD(S634A) (lane 4). AIR-2 autophosphorylation (P-AIR-2) was also significantly increased in the presence of TLK-1KD or TLK-1KD(S634E) (lanes 3 and 5).
(D) Quantitation of histone H3 phosphorylation in the kinase assays shown in (C). Error bars represent the standard deviation from at least three separate experiments.