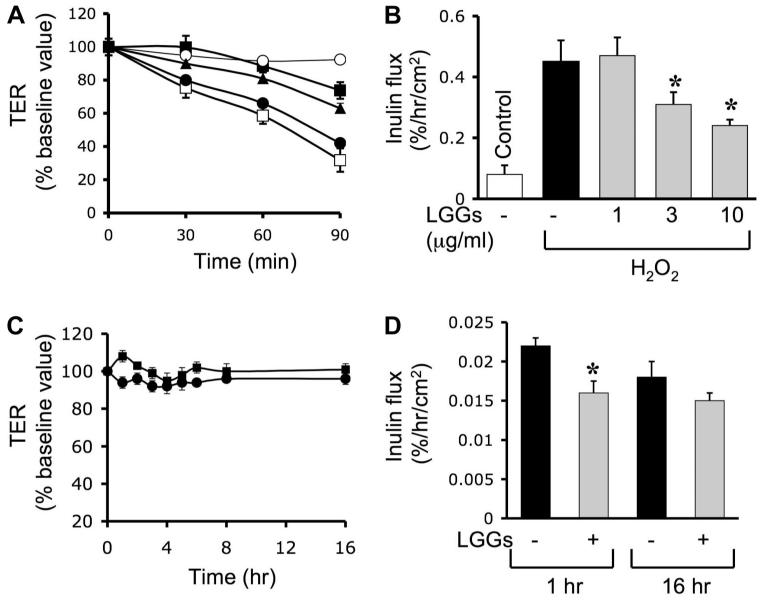
Fig. 1.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) culture supernatant (LGG-s) prevents H2O2-induced paracellular permeability. A and B: Caco-2 cell monolayers were incubated with or without H2O2 (20 μM) in the absence (□) or presence of 1 μg/ml (●), 3 μg/ml (▲), or 10 μg/ml (■) of LGG-s (unpurified LGG growth medium, administered 30 min prior to H2O2). Transepithelial resistance (TER; A) was measured at varying times, and inulin flux (B) was measured at 2 h after H2O2 administration. C: TER was measured in cell monolayers treated with (□) or without (○) probiotics in the absence of H2O2. Values are means ± SE (n = 8; n includes values from 4 independent experiments). D: inulin flux was measured in cell monolayers treated with or without LGG-s in the absence of H2O2 at 1 or 16 h. Values are means ± SE (n = 8). *Significantly (P < 0.05) different from corresponding values for cell monolayers without LGG-s treatment.