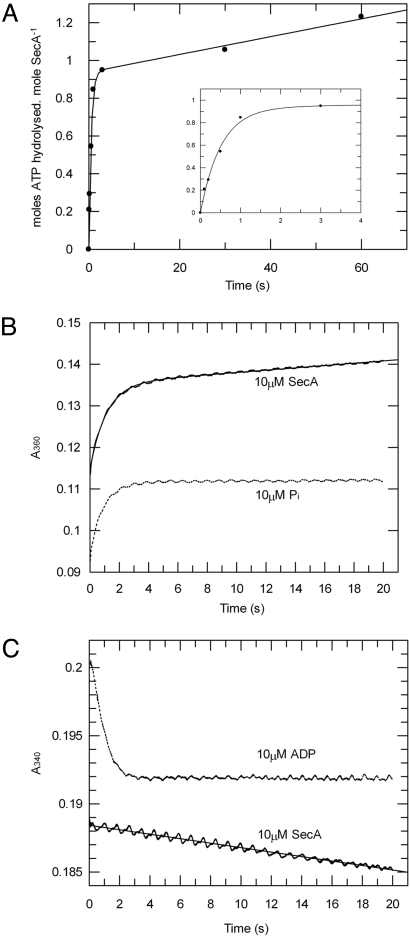
Fig. 3.
Transient kinetic analysis of SecA ATPase activity shows that ADP release is rate-limiting in the hydrolytic cycle. The pre-steady-state ATPase activity of SecA was measured in the presence of 1 mM ATP and 2 mM MgCl2. (A) The data from quenched-flow rapid mixing were fitted to Eq. 4 (SI Equations), to reveal kcleave as 1.9 s−1. (Inset) Expanded plot of the first 4 s. (B) Release of phosphate during ATP hydrolysis by 10 μM SecA was measured by stopped-flow rapid mixing using the EnzChek kit and compared with a control produced by mixing equimolar phosphate (10 μM) with the assay components (dotted line). The data for the ATPase (solid line) were fitted to Eq. 4 (SI Equations), determining kcat to be 0.013 s−1. (C) Release of ADP during ATP hydrolysis by SecA was measured by stopped-flow rapid mixing, using an enzyme-linked assay for ADP. As a control, the trace produced by mixing 10 μM ADP with the assay components is shown (dotted line). The data for the ATPase reaction (solid line) were fitted to a straight line to deduce the value for kcat as 0.013 s−1.