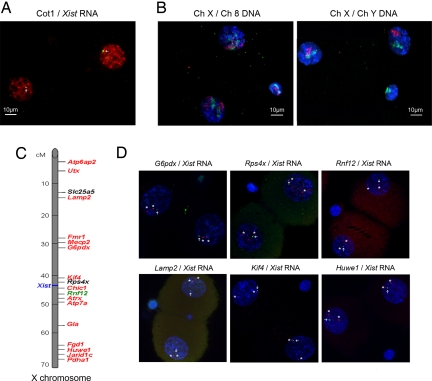
Fig. 1.
Transcriptional activity of the paternal X chromosome assayed by gene RNA FISH in 2-cell embryos. (A) Deconvolved images of 3D stacks of a representative 2-cell female embryo labeled for RNA FISH with an Xic-specific probe (green) and Cot 1 RNA (red). Cot 1 is present at the site of the Xist RNA. (B) Deconvolved images of 3D stacks of a representative 2-cell embryo labeled for DNA FISH. Left: Female embryo with an Xic-chromosome probe (green) and chromosome 8 probe (red). Right: Male embryo with an Xic-chromosome probe (green) and chromosome Y probe (red). Y chromosome is not present in the second polar body. All of the chromosomes territories are dispersed. (C) X-chromosome map with the 18 studied genes. In red, genes that were shown to be fully or partially repressed during spermatogenesis in round spermatids (14); in green, gene that was shown to be reactivated in round spermatids (14); in black, genes that have been not studied in Namekawa and colleagues' report (14). (D) Representative 2-cell female embryos are shown for Xist transcript (green), gene primary transcripts (red), and DAPI (blue). Two gene signals can be seen in each blastomere of 2-cell embryos.