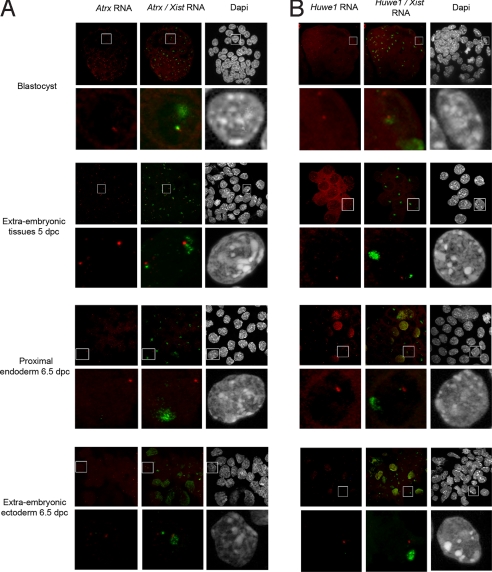
Fig. 4.
Specific profile of Atrx and Huwe1 transcriptional activity during X-imprinted inactivation assayed by RNA FISH in pre- and postimplantation stages. (A) Atrx primary transcript signals (red) using specific RNA FISH at blastocyst stage (Top), in extraembryonic tissues at 5 dpc (Upper Middle), proximal endoderm (Bottom Middle), and extraembryonic ectoderm at 6.5 dpc (Bottom). A loss of Atrx signal from the paternal allele was observed in the trophectoderm at the blastocyst stage. Activity from the paternal allele was observed in extraembryonic tissue as early as 5 dpc, as assessed by the presence of 2 Atrx signals. This pattern was confirmed in extraembryonic tissue at 6.5 dpc. Only 1 signal, distant from the Xist RNA domain, was observed in proximal endodermic cells at 6.5 dpc. (B) Huwe1 primary transcript signals (red) using specific RNA FISH at blastocyst stage (Top), in extraembryonic tissues at 5 dpc (Upper Middle), proximal endoderm (Bottom Middle), and extraembryon or embryon at 6.5 dpc (Bottom). Two signals are present, 1 within the Xist domain (green), at the blastocyst stage. The paternal allele is silenced in the extraembryonic tissues as early as 5 dpc because only 1 signal, near the maternal Xist pinpoint, persists. The same pattern was observed in extraembryonic tissues at 6.5 dpc.