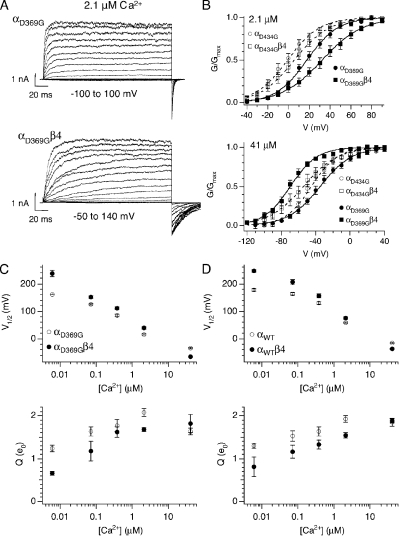
Figure 5.
Ca2-dependent effects of β4 on mutant BK channel G-V. (A) A family of currents from αD369G BK channels composed of either the pore forming alone (top) or with the β4 auxiliary subunits (bottom). Recorded in 2.1 µM Ca2+, currents were evoked in response to 200-ms depolarizations. (B, top) Effect of β4 on mslo and hslo mutant G-V relations at 2.1 µM Ca2+ (hslo_αD434G: n = 7; hslo_αD434G β4: n = 9; mslo_αD369G: n = 22; mslo_αD369G β4: n = 32). (B, bottom) Effect of β4 on mslo and hslo mutant G-V relations at 41 µM Ca2+ (hslo_αD434G: n = 10; hslo_αD434G β4: n = 11; mslo_αD369G: n = 18; mslo_αD369G β4: n = 15). Symbols represent mean G/Gmax data, curves represent fits to the Boltzmann function, and error bars represent SEM. (C) Effects of β4 on steady-state gating of mutant channels. Mean V1/2 (top) and mean effective gating charge (Q) values (bottom) plotted as a function of Ca2+. Error bars represent SEM. (D) Effects of β4 on steady-state gating of wild-type channels. Mean V1/2 (top) and mean effective gating charge (Q) values (bottom) plotted as a function of Ca2+. Error bars represent SEM.