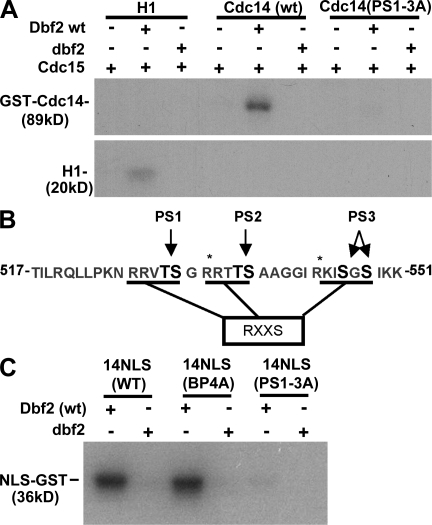
Figure 3.
Cdc14 is phosphorylated by Dbf2–Mob1. (A) Phosphorylation of Cdc14 by Dbf2–Mob1. Purified GST-Cdc14, GST-Cdc14(PS1–3A), or histone H1 were treated with wild-type (wt) or kinase-dead Dbf2–Mob1 (dbf2) complex. Dbf2–Mob1 was activated in vitro by protein kinase Cdc15. Phosphorylated Cdc14 was detected by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. PS1–3A refers to a hextuple mutant in which the residues in PA pairs 1–3 (PS1–3; B) were changed to Ala. (B) The C terminus of Cdc14 contains three potential regions of Dbf2–Mob1 phosphorylation. The sites that were altered for this study, PS1–3, are indicated in black font. RXXS refers to the preferred site for phosphorylation by Dbf2 (Mah et al., 2005). (C) Phosphorylation of Cdc14’s NLS region by Dbf2–Mob1 depends on PS1–3. The last 100 amino acids of the C terminus of Cdc14 were fused to GST. Purified GST-NLS was treated with either wild-type Dbf2–Mob1 or kinase-dead Dbf2–Mob1. Dbf2–Mob1 complexes were activated with protein kinase Cdc15. Phosphorylation of wild type, a BP mutant, BP4A (Fig. 1 A), and a six-site Ser/Thr to Ala mutant, PS1–3A, were assayed. Asterisks indicate predicted trypsin cleavage sites.