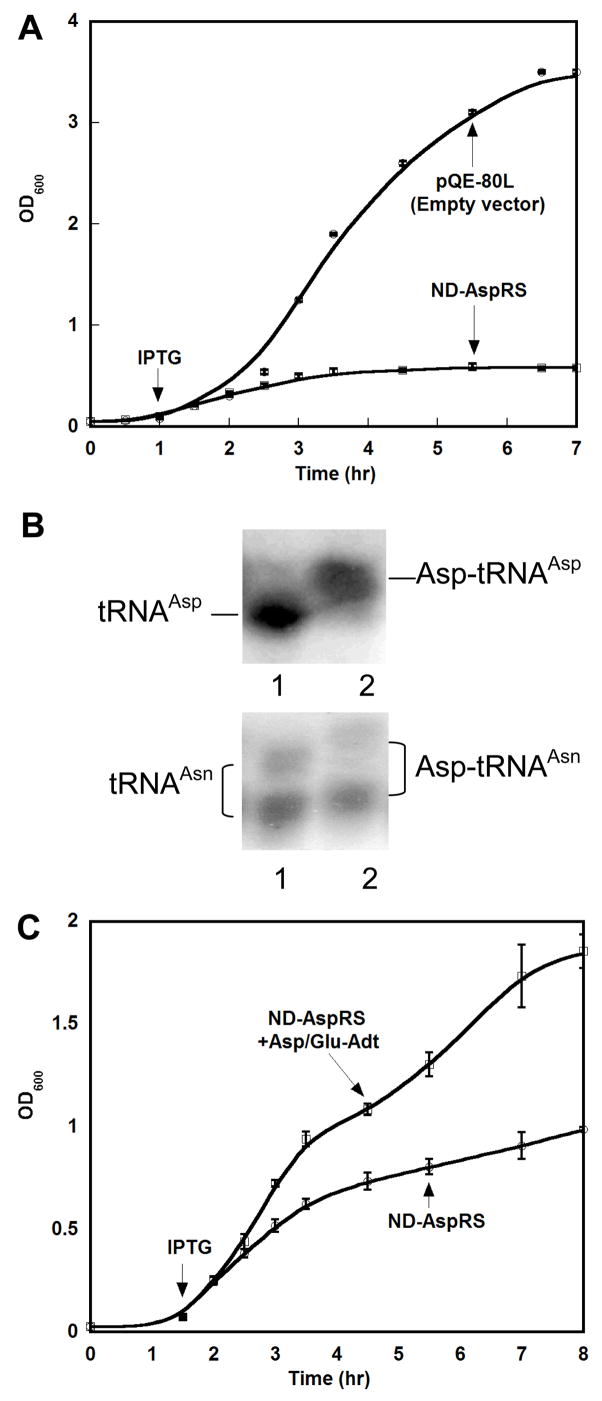
Figure 1. Heterologous expression of H. pylori ND-AspRS is toxic to E. coli and can be rescued by co-expression of the H. pylori Asp/Glu-Adt.
A. Overexpression of Hp ND-AspRS was monitored upon induction with IPTG. This overexpression was toxic to E. coli, when compared to a cell culture containing the empty plasmid, pQE-80L, grown under identical conditions. B. ND-AspRS aminoacylates E. coli tRNAAsp (top gel) and misacylates E. coli tRNAAsn (bottom gel) (37, 17). In each gel, lane 1 is a deacylated tRNA control and lane 2 represents the tRNA pool treated with Hp ND-AspRS. Primers specific for tRNAAsp (top) or tRNAAsn were used for Northern Blot analyses to specifically visualize each tRNA of interest. The upward shift of the two bands in lane 2 demonstrates ND-AspRS aminoacylates E. coli tRNAAsn, consistent with the toxicity of this enzyme when overexpressed in E. coli. C. The toxicity of ND-AspRS overexpression can be alleviated by co-overexpression of H. pylori Asp/Glu-Adt (GatCAB). See Experimental Methods for details. All growth curves and acid gels were conducted in triplicate.