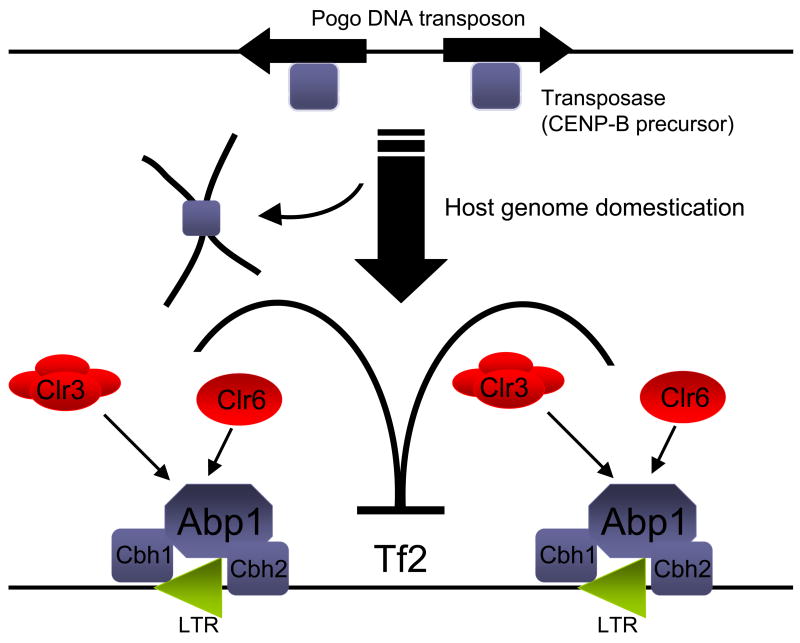
Figure 1. Taming of transposon-derived proteins mediates CENP-B surveillance of Tf2 elements.
The CENP-B proteins, Abp1, Cbh1 and Cbh2, are derived from the transposase of pogo DNA transposons. These proteins bind alpha satellite repeats and facilitate centromere formation. During evolution, an ancient CENP-B precursor also acquired the ability to bind Tf long terminal repeats (LTRs). This new function was likely co-opted by S. pombe for the purpose of controlling the mobility of Tf retroelements. Cam et al provide evidence that Abp1 may recruit the other two CENP-B homologues, Cbh1 and Cbh2, to Tf2 LTRs. The Clr3 and Clr6 histone deacetylases, which also have an important role in retrotransposon silencing, may help Abp1 recruit Cbh1 and possibly Cbh2 to Tf2 LTRs.