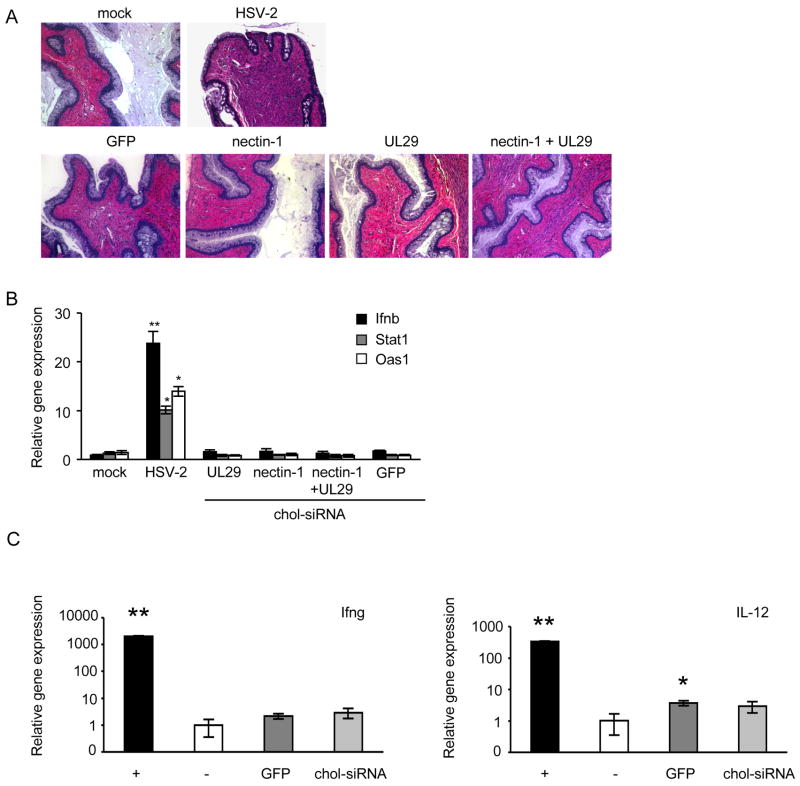
Figure 6. Chol-siRNAs do not cause inflammation or activate interferon-response genes.
Vaginal tissue was harvested from mice 1 day following the second of 2 treatments with either 2 nmol chol-siRNA (no HSV-2), with HSV-2 only as a positive control or with PBS (mock) and divided for analysis by hematoxylin and eosin staining (A, x10 magnification) or for RNA extraction for qRT-PCR analysis of interferon-responsive genes Ifnb (black), Stat1 (grey) and Oas1 (white) (B). The chol-siRNAs did not induce inflammation or interferon-responsive gene expression. (C) RNA was also extracted from vaginal tissue of mice treated with 2 nmol chol-siRNA twice (without OF) 1 day following the second treatment, and analyzed by qRT-PCR for Ifng (left) and IL12 (right). Positive controls (+, black) were anti-CD3/CD28 activated T cells (Ifng) and LPS-activated splenocytes (IL12). PBS-treated vaginal tissues served as negative control samples (−, white). siRNAs either targeted GFP (dark grey) or nectin-1 (light grey). Relative gene expression compared to gapdh (mean±S.D.) is shown. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.001.