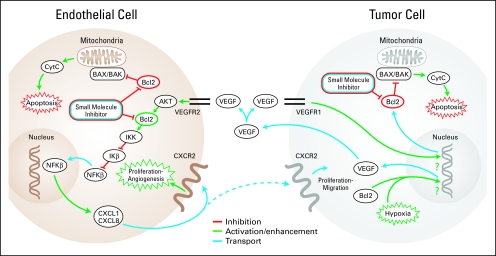
Fig 1.
Role of Bcl-2 in tumor cell and endothelial cell apoptosis and survival. Diagram depicts the involvement of Bcl-2 in tumor cell and endothelial cell function, as well as in the regulation of cross-talks between the two cell types. Bcl-2 is a pivotal checkpoint in the apoptotic pathway, inhibiting the proapoptotic actions of Bax and Bak. Both Bcl-2 expression and hypoxia may result in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production, which is secreted by the tumor cell. Endogenous VEGF can bind to VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1) on tumor cells sending a prosurvival signal, upregulating Bcl-2 production, or can also bind to VEGFR2 on endothelial cells, promoting cell survival and stimulating proliferation and angiogenesis via Bcl-2–dependent pathways.