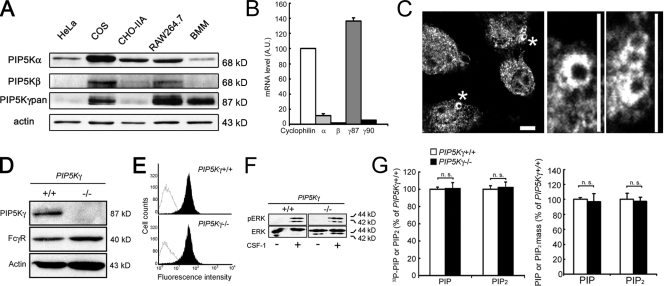
Figure 1.
Characterization of PIP5K-γ in BMM. (A) Western blot of endogenous proteins in WT BMM. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR. The PIP5K level in WT BMM was normalized against cyclophilin (n = 3). (C) Recruitment of PIP5K-γ to the phagocytic cup. WT BMM exposed to IgG-opsonized particles were stained with anti–PIP5K-γpan antibody. The middle and right panels show enlarged views of regions marked by asterisks. Bars, 10 µm. (D) Western blot of PIP5K-γ−/− BMM. (E) FACs analysis of surface accessible FcγR. Black peaks, surface FcγR fluorescence; white peak, background. (F) CSF-1–induced ERK activation. CSF-1–stimulated BMM were extracted for Western blotting with anti-ERK and -pERK. (G) Phosphoinositide analyses. The PIP2 or PIP value in PIP5K-γ−/− BMM was expressed as the percentage of WT cells. Left, TLC (n = 3). Right, HPLC (n = 4). Error bars indicate SEM. n.s., not significant.