Fig. 2. Lmx1a expression is less restricted in mutants.
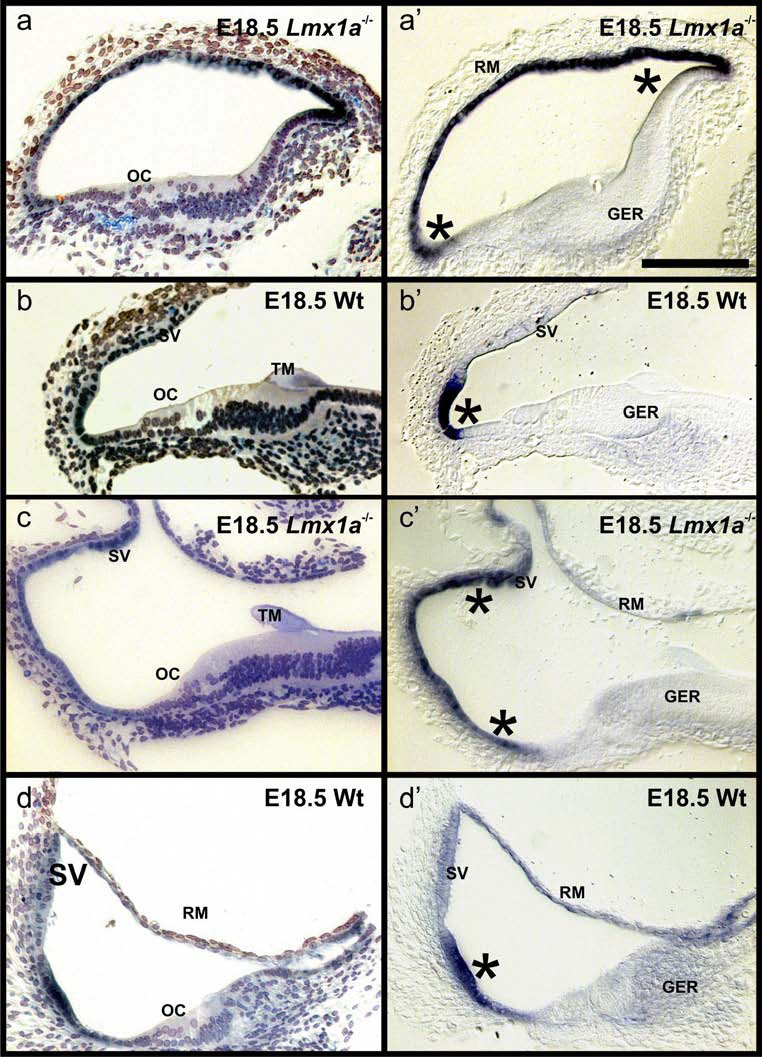
These sections show the distribution of Lmx1a ISH reaction product in wildtype (B,D) and Lmx1a mutant mice of embryonic day 18.5. The ears were reacted for whole mount in situ hybridization (see Fig. 1), embedded in soft epoxy resin and sectioned at 5–10 µm. These radial sections show a well organized organ of Corti (OC) with one inner and 3–4 rows of outer hair cells in the wildtype (B,D). In contrast, hair cells are disorganized in the Lmx1a mutant mice (A,C). Nevertheless, the main medial-to-lateral areas of the cochlea such as greater epithelial ridge (GER) with a tectorial membrane (TM), OC and lateral wall are distinct. In wildtype mice the Lmx1a in situ signal is in the lateral wall (asterisk) adjacent to the stria vascularis (SV; B’, D’). In contrast, in the Lmx1a mutant mice the strong Lmx1a in situ signal expands to include the stria vascularis (asterisks) or even Reissner’s membrane (RM; A’,C’). Bar in A’ indicates 100 µm for all images.
