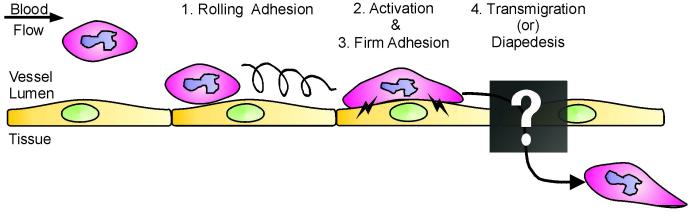
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the leukocyte adhesion and transmigration cascade. Given an inflammatory stimulus, leukocytes initially loosely adhere on the vascular ECs, rolling along the blood vessel wall via transient selectin-mediated interactions (1). During the activation stage, both the EC and leukocyte begin to upregulate expression and/or activity of adhesion receptors on the cell surfaces (2), and this is required for initiating the firm adhesion stage (3). Finally, leukocytes exit the bloodstream, crossing the endothelium by the process known as transmigration or diapedesis (4). The mechanisms and pathways by which transmigration occurs are poorly understood and thus will be the focus of this review.