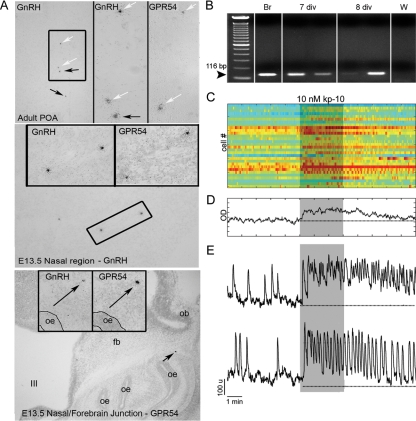
Figure 3.
GnRH-1 neurons express a functional receptor to kp-10. A, In situ hybridization histochemistry for GnRH-1 mRNA and gpr54 mRNA performed on alternate sections from an adult mouse brain (upper panel) and E13.5 mouse sections (middle and lower panels). In agreement with the literature, in the adult brain preoptic area (POA; top), a subset of GnRH-1 neurons express gpr54 transcript (white arrows, boxed area is shown on the right for GnRH-1 and gpr54, and arrows point to cells shown in higher magnification). Gpr54-expressing cells, like GnRH-1-expressing cells, were detected at E13.5 in the nasal area (middle panel) and at the nasal/forebrain junction (bottom panel). oe, Olfactory epithelium; ob, olfactory bulb; fb, forebrain; III, third ventricle. B, Gel of PCR products from single-cell RT-PCR performed on GnRH-1 cells extracted from nasal explants after 7 or 8 d in vitro (div) using specific primers for gpr54. Seventy percent of the tested cells (n = 37) exhibited a band with gpr54-specific primers. Adult brain (Br) showed the expected band, whereas water (W) is negative. C, Effect of kp-10 on intracellular calcium level in 30 cells simultaneously recorded. Each row represents color-coded changes in intracellular calcium in a single cell. D, Average value of intracellular calcium level over time in 30 cells shown in C. E, Two representative traces of responding cells (85% of the cells), which either exhibited summation of single calcium spikes, termed plateau-bursting type of calcium signal (upper panel), or an increase in the frequency of calcium oscillations (lower panel). Note the long-lasting effect of kp-10 on calcium signaling after washout of agonist.