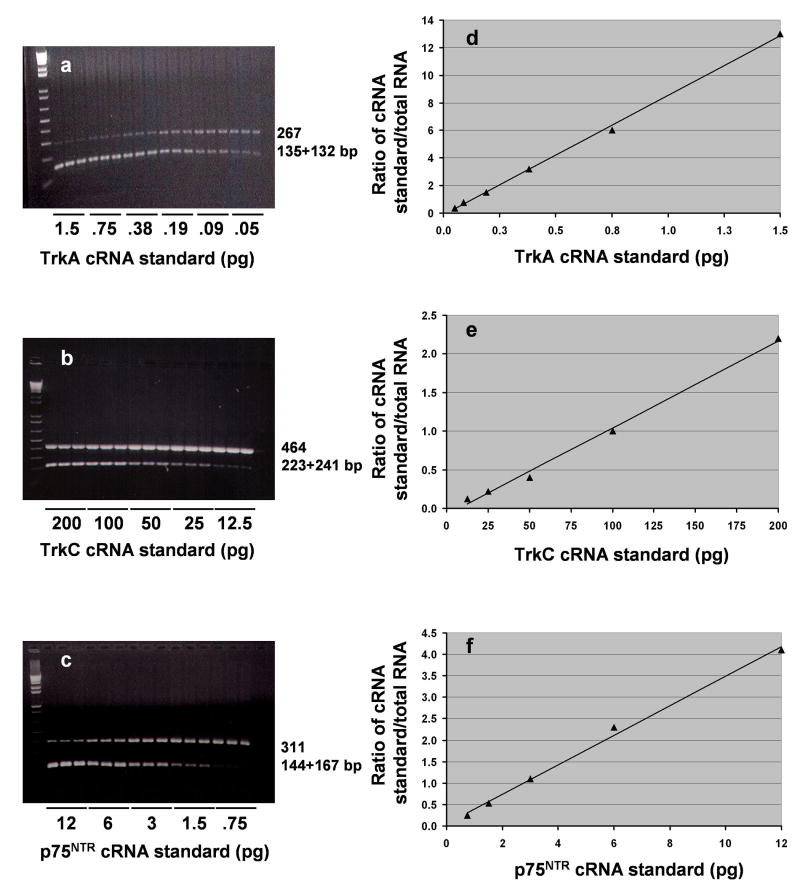
Figure 1.
Representative gel electrophoreses showing competitive PCR analysis for TrkA (a), TrkC (b), or p75NTR (c) mRNA contents in PFC obtained from one normal control subject. Decreasing concentrations of internal standard cRNA (TrkA, 1.5-0.05 pg; TrkC, 200-12.5 pg; p75NTR, 12-0.75) were added to a constant amount (1 μg) of total RNA. The mixtures were reverse transcribed and PCR-amplified in the presence of trace amounts of [32P]dCTP; aliquots were electrophoresed on 1.5% agarose gel. The higher molecular size band corresponds to the amplification product arising from the mRNA, whereas the lower bands arise from cRNA generated from the internal standard. Data derived from the agarose gel are plotted as the counts incorporated into the amplified TrkA (d), TrkC (e), or p75NTR (f) cRNA standard divided by the counts incorporated into the corresponding mRNA amplification product versus the known amount of internal standard cRNA added to the test sample. The point of equivalence represents the amount of the respective mRNA.