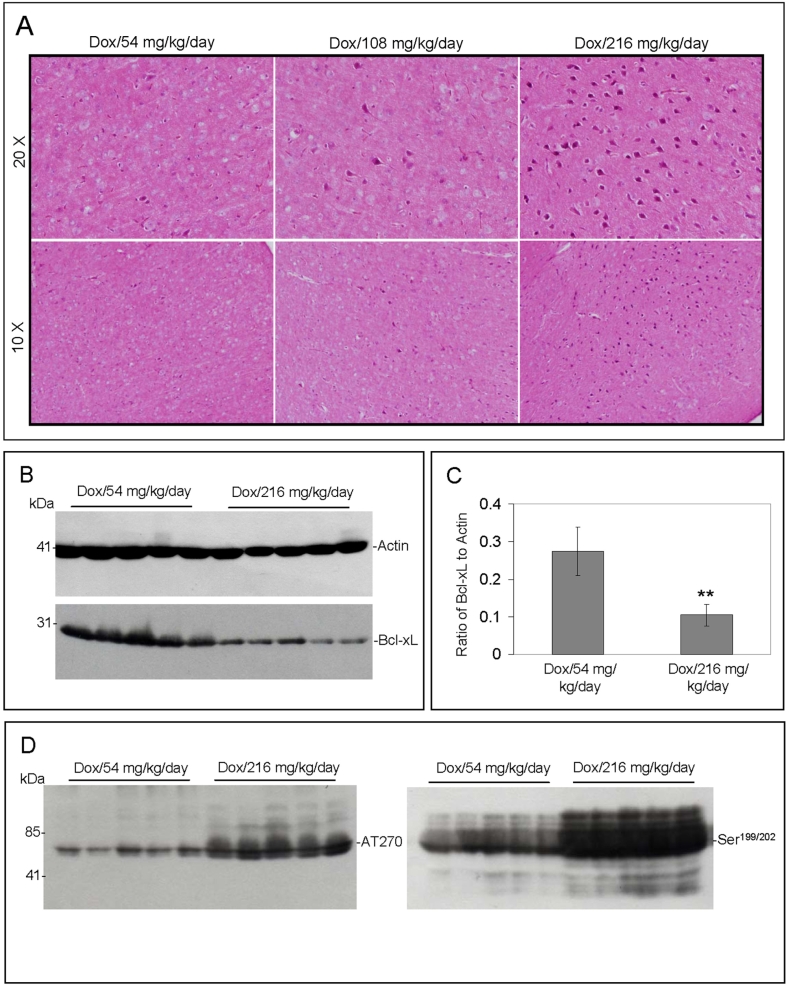
Figure 1.
Oral administration of dox results in increased neuronal damage and tau phosphorylation with decreased Bcl-xL expression dose dependently in GT-tg mice. A. Mouse brain coronal frozen sections were stained with H&E. Left column indicates PSAPP mice receiving dox, middle column indicates PSAPP/Tat mice without dox and right column indicates PSAPP/Tat mice receiving dox. B. Bcl-xL expression was analyzed by Western blotting analysis of the mouse brain homogenates with anti-Bcl-xL antibody. C. Densitometry analysis shows the band density ratio of Bcl-xL to actin. D. Western blot analysis by antibody AT270 (left) or Ser199/202 (right) shows phosphorylated tau protein.