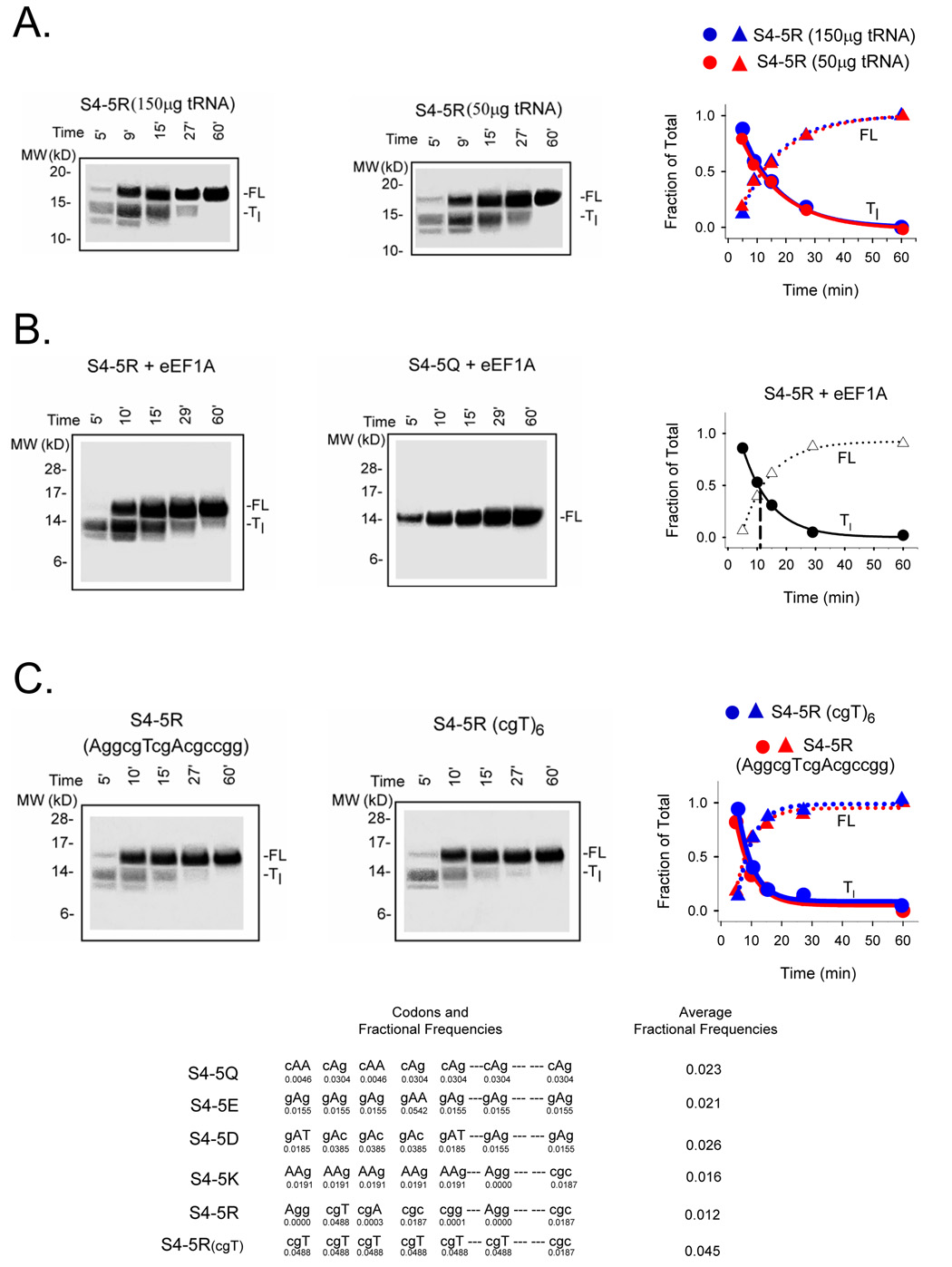
Figure 4. Potential factors in charge-dependent pausing.
A. Addition of supplemental tRNAs. Translation reactions were set up exactly as described in the Materials and Methods and Figure 2, but calf liver tRNAs (100 µg/ml; Novagen) was added to give a total of 150 µg/ml tRNAs in the translation reaction. Samples were fractionated on NuPAGE gels (Bis-Tris 12%; lanes 1–5 loaded with 22, 15, 5, 3, and 3 µl, respectively). Data are plotted as fraction of Tl and FL for the indicated times to give a Tc value of ~12 min. B. Addition of supplemental eEF1A. Translations were carried out as described in the Materials and Methods and Figure 2, but in the presence of additional purified eEF1A as described in the text. Samples were fractionated on NuPAGE gels (Bis-Tris 12%; lanes 1–5 loaded with 20, 10, 5, 3, and 1.5 µl, respectively). The data are plotted as fraction of Tl and FL for the indicated times to give a Tc value of ~12 min. C. Rare vs common codons. An S4-5R construct containing 5 consecutive arginines was translated as described in Figure 1. Samples were fractionated on NuPAGE gels (Bis-Tris 12%; lanes 1–5 loaded with 25, 15, 5, 3, and 2.5 µl, respectively). The gel on the left derives from a peptide encoded by the 5 consecutive arginine codons AggcgTcgAcgccgg, some of which are rare codons. The gel on the right derives from a peptide encoded by 5 consecutive cgT codons plus a sixth cgT (R3), which are common. A plot of the fraction of Tl and FL for the indicated times gives Tc values of 10.2 ± 1.8 (n = 2) and 10.4 min, respectively. Below are the average fractional frequencies of occurrence for the 7 codons in each construct (see Figure 2), based on the study of Thanaraj and Argos 37.