Figure 7.
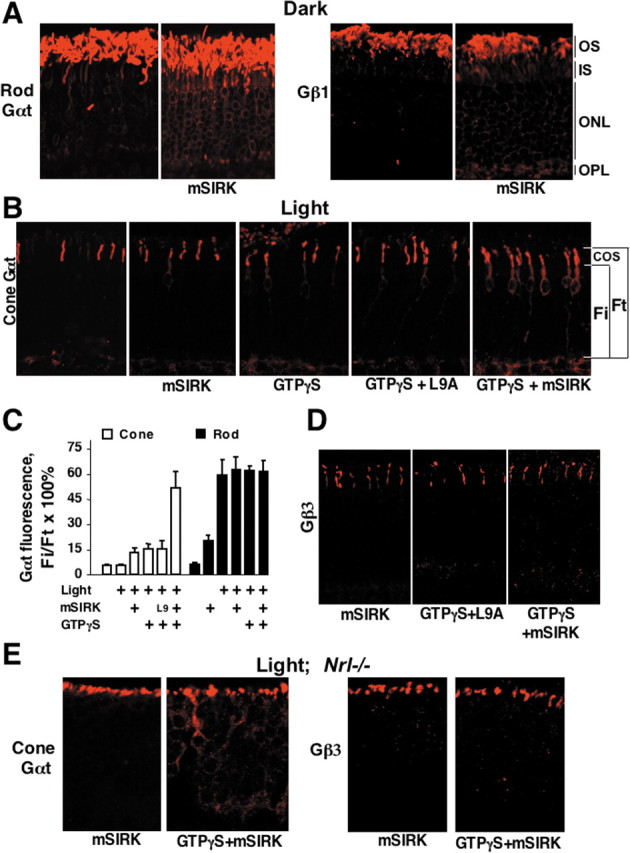
Translocation of rod and cone transducins is facilitated by the synthetic Gβ-binding peptide mSIRK. A, Dark-adapted retinas were permeabilized with α-toxin and incubated in the dark in the presence or absence of 50 μm mSIRK. After 1 h, the retinas were fixed, and the localization of rod Gαt and Gβ1 was determined. B, Dark-adapted retinas were permeabilized with α-toxin and treated with 50 μm mSIRK or its inactive mutant (L9A) peptide in the presence or absence of 100 μm GTPγS. Retinas were then exposed to sunlight for 15 min, fixed, sectioned, and stained with antibodies against cone Gαt. C, Quantification of the data from a series of experiments including one shown in B. Rod or cone Gαt immunofluorescence in the entire photoreceptor (Ft) and immunofluorescence from the inner compartments (Fi) were determined as described in Figure 2 and Materials and Methods. The average Fi/Ft ratio (mean ± SD) in each experiment was determined within three areas of the retina. The data were collected in at least six independent batches of retinas (groups of mice). Retinas were dissected under dim red light and permeabilized in the presence of GTPγS, mSIRK, L9A mutant, or mSIRK with GTPγS as indicated. For L9A plus GTPγS, n = 3. The concentration of mSIRK or L9A was 50 μm. Light intensities varied from 500 lux to direct sunlight, providing identical results. Control permeabilized retinas were kept in the dark. D, Localization of cone Gβγ (Gβ3 immunoreactivity) in permeabilized wild-type mouse retinas treated with mSIRK, L9 with GTPγS, and mSIRK with GTPγS, in light. This is representative of three independent experiments. E, Retinas of Nrl−/− mice were permeabilized and treated with mSIRK or mSIRK with GTPγS, in light (1000 lux or direct sunlight for 5 or 30 min produced identical results). Localization of cone Gαt and Gβ3 was determined by immunofluorescence microscopy.
