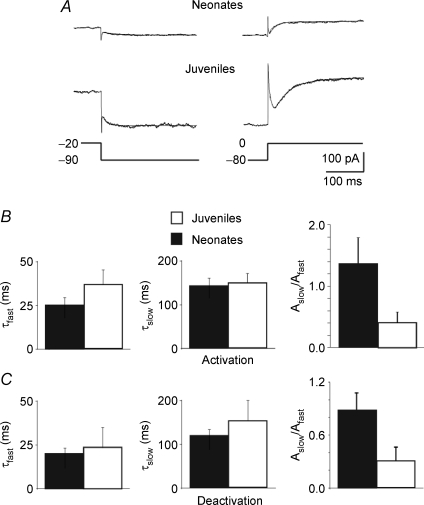
Figure 4. Similar kinetic properties of linopirdine-sensitive currents recorded in neonatal and juvenile neurons.
A, linopirdine-sensitive currents deactivated by 1 s voltage step from −20 to −90 mV (left) and activated (right) by 1 s voltage step from −80 to 0 mV. Each trace (average of 3 traces) could be fitted with the sum of a fast and a slow exponential. B and C, each bar represents the mean fast (τfast) and slow (τslow) components as well as their relative fractions Aslow/Afast of deactivated (C) and activated (B) linopirdine-sensitive currents obtained in neonatal (black; n = 7) and in juvenile neurons (white; n = 5) as in A.