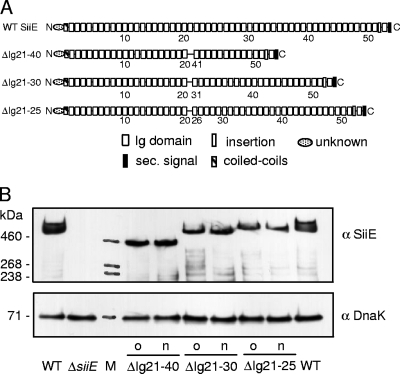
FIG. 2.
Oligonucleotide-based recombineering of SPI4-encoded SiiE. (A) Schematic representation of the domain organization of siiE encoding a giant nonfimbrial adhesin in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium. Oligonucleotide-mediated recombinant engineering was performed to delete regions encoding the 5, 10, or 20 immunoglobulin (Ig) domain as indicated. Deletions between the Ig repeats were in frame without introduction of a scar or additional alterations. WT, wild type; sec., secretion. (B) Synthesis of SiiE and derivatives by Salmonella wild-type and various mutant strains harboring deletions of the entire siiE gene or in-frame deletions of the 5, 10, or 20 Ig domains. Bacterial cultures were subcultured in LB for 3.5 h. Equal amounts of cells, adjusted by using optical density at 600 nm, were harvested, and proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on gradient gels. Proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes, and SiiE was detected by incubation with antiserum against SiiE (α SiiE). As loading controls, Western blots were probed with antiserum against DnaK (StressGen) (α DnaK). The sizes of SiiE variants from mutant strains (o) were described previously (5) and strains generated in this study (n) were compared. Lane M contained high-molecular-weight protein standards.