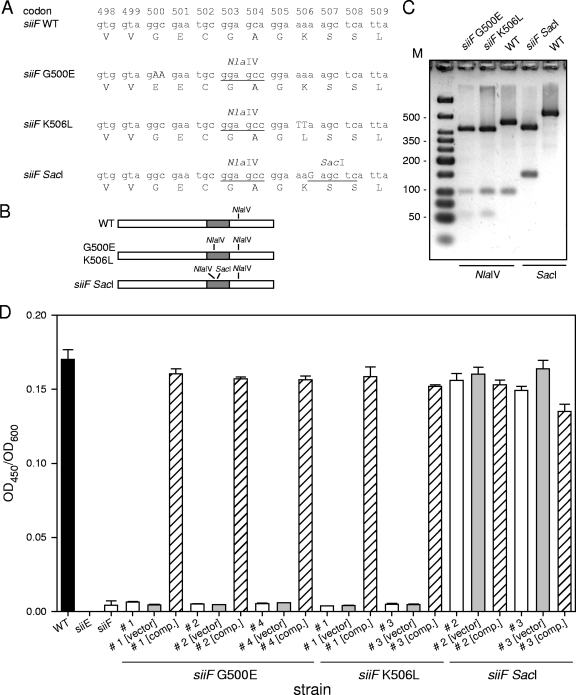
FIG. 3.
Site-directed mutagenesis of chromosomal siiF in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium. (A) Sequence of the target region in siiF encoding the putative ABC and design of site-directed mutations and silent mutations. All manipulations resulted in a silent mutation that generated a novel NlaIV site at codons 503 and 504. In addition, mutations G500E and K506L resulted in amino acid changes in the ABC of SiiF. Mutation siiF SacI introduced an additional SacI site without altering the amino acid sequence of the ABC. Newly introduced restriction sites are underlined, and mutations resulting in amino acid changes are indicated by capital letters. WT, wild type. (B) Predicted restriction map for a 500-bp PCR product of siiF obtained for wild-type and various mutant strains. The gray box indicates the mutagenesis target region. (C) The PCR products for fragments of siiF from wild-type and representative clones of various mutant strains were subjected to restriction analyses with NlaIV or SacI as indicated. Lane M contained a DNA size marker. (D) The secretion of SiiE by Salmonella wild-type and various mutant strains was analyzed by an ELISA for SiiE. The Salmonella wild-type strain (black bar), mutant strains with deletions of the entire siiE or siiF gene, selected clones (indicated by number signs) with site-directed mutations in siiF (open bars), and mutant strains harboring the plasmid vector pWSK29 (vector) (gray bars) or plasmid p3223 for expression of wild-type siiF (comp.) (hatched bars) were grown in LB medium, and culture supernatants were collected for quantification of SiiE by ELISA. The values for SiiE (optical density at 450 nm [OD450]) were normalized by using the culture density (optical density at 600 nm [OD600]).