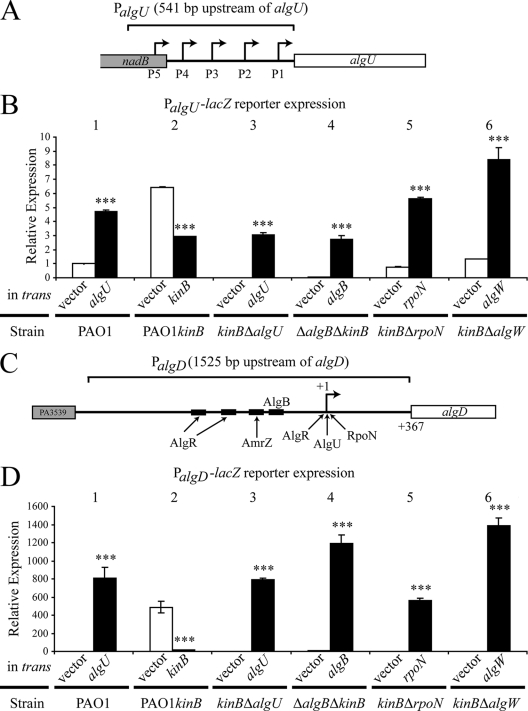
FIG. 3.
Loss of kinB causes upregulation of both PalgU and PalgD. β-Galactosidase activity from PalgU-lacZ and PalgD-lacZ reporters on the chromosomes of PAO1, PAO1 kinB::aacC1, and PAO1 kinB::aacC1 isogenic mutants was determined. PalgU-lacZ and PalgD-lacZ reporter constructs were integrated into the chromosomes of the indicated strains. Genes indicated were expressed in trans from the PBAD promoter of pHERD20T. β-Galactosidase activities were determined after 24 h of growth on PIA with 0.1% arabinose. Values were normalized to PAO1 pHERD20T (empty vector) reporter expression and indicated as means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. Student's t test was performed for comparison of activity of the strain with vector only or with the complementing gene in trans. Asterisks indicate significant differences (***, P < 0.0001). Strain PAO1 kinB::aacC1 is indicated as PAO1 kinB. Note that expression of algU in PAO1 is a positive control for the analysis due to the AlgU-dependent nature of both PalgU and PalgD. (A) A schematic of the entire PalgU promoter region with the relative positions of the five promoters that were utilized for the lacZ promoter fusion. (B) PalgU activity in PAO1, PAO1 kinB::aacC1, and strains isogenic to PAO1 kinB::aacC1. High PalgU activity in PAO1 kinB::aacC1 and PAO1 ΔkinB mutants requires algU, algB, rpoN, and algW. Note that kinB expression significantly lowers PalgU activity. (C) A schematic of the entire PalgD promoter region that was used for the lacZ promoter fusion. The relative binding sites of the PalgD transcriptional activators are indicated. (D) PalgD activity in PAO1, PAO1 kinB::aacC1, and strains isogenic to PAO1 kinB::aacC1. High PalgD activity in PAO1 kinB::aacC1 and PAO1 ΔkinB requires algU, algB, rpoN, and algW. Note that kinB expression significantly lowers PalgD activity.