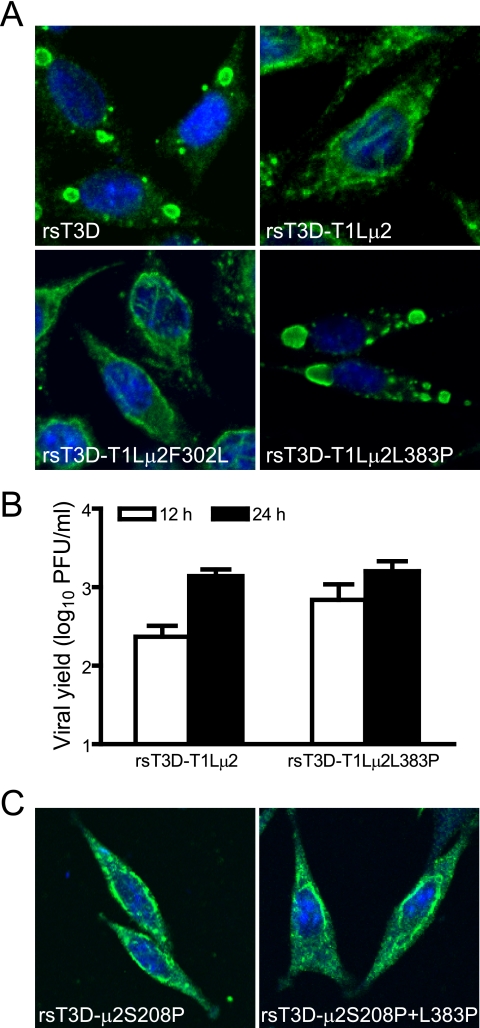
FIG. 9.
Effect of altering μ2 amino acids other than at position 208 on viral inclusion morphology and growth. (A) Inclusion morphology of viruses with alterations in T1L μ2. L cells were infected at an MOI of 2 PFU/cell with wt viruses or viral mutants with substitutions at amino acid positions 302 and 383 in the T1L μ2 protein. At 24 h postinfection, cells were imaged using confocal immunofluorescence microscopy after staining with μNS-specific antiserum (green). Nuclei were stained with TO-PRO3 (blue). rsT3D, wt strain; rsT3D-T1Lμ2, rsT3D containing T1L-derived μ2; rsT3D-T1Lμ2F302L, rsT3D-T1Lμ2 with a Phe302-to-Leu substitution in μ2; rsT3D-T1Lμ2L383P, rsT3D-T1Lμ2 with a Leu383-to-Pro substitution in μ2. (B) Growth of virus with substitutions at amino acid position 383 of T1L μ2. L cells were infected with the indicated viruses at an MOI of 2 PFU/cell, and titers in culture lysates were determined by plaque assay after 0, 12, and 24 h of incubation. Results are mean viral yields (relative to time zero) from three independent experiments. Error bars denote standard deviations. (C) Inclusion morphology of viruses with alterations in T3D μ2. L cells were infected with the indicated viruses and imaged 24 h later as described for panel A. rsT3D-μ2S208P, rsT3D containing a Ser208-to-Pro substitution in μ2; rsT3D-μ2S208P+L383P, rsT3D with Ser208-to-Pro and Leu383-to-Pro substitutions in μ2.