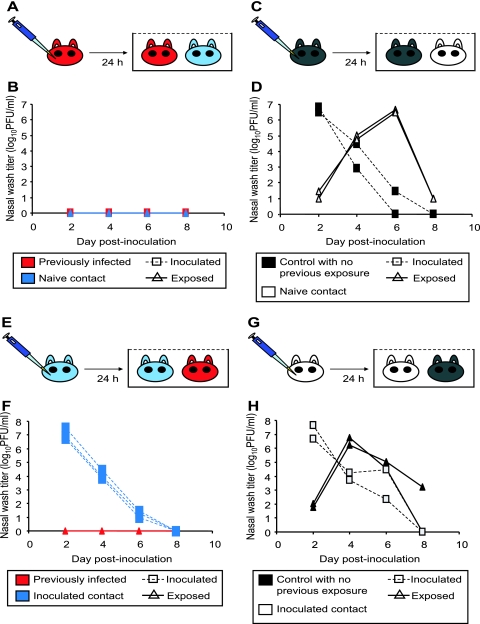
FIG. 2.
Previously infected guinea pigs exhibit sterilizing immunity to homologous challenge. (A) Schematic representation of challenge by the intranasal route. Three previously infected guinea pigs (red) were challenged intranasally with Pan/99 virus. At 24 h postinoculation, a naïve contact animal (blue) was cocaged with each of the three inoculated guinea pigs. (B) Results of homologous challenge by the intranasal route. No virus was detected in the nasal washings of challenged guinea pigs (red squares with dashed lines), and no virus was detected in the naïve contact animals (blue triangles with solid lines). (C) Schematic representation of challenge of control guinea pigs by the intranasal route. Two control animals with no previous exposure (black) were inoculated intranasally with Pan/99 virus. At 24 h postinoculation, a naïve contact guinea pig (white) was cocaged with each of the two inoculated guinea pigs. (D) Results of Pan/99 challenge of control guinea pigs by the intranasal route. Animals with no previous exposure were productively infected through inoculation (black squares with dashed lines) and transmitted efficiently to naïve contact animals (white triangles with solid lines). (E) Schematic representation of challenge through exposure to an infected guinea pig. Three naïve guinea pigs were inoculated intranasally with Pan/99 virus. At 24 h postinoculation, each of the three acutely infected animals (blue) was placed into the same cage with one previously infected guinea pig (red). (F) Results of homologous challenge through exposure to an infected guinea pig. Intranasally infected contact animals shed high titers of virus into nasal washes (blue squares with dashed lines); however, guinea pigs with previous exposure to Pan/99 virus (red triangles with solid lines) did not become infected through contact with the infected animals. (G) Schematic representation of challenge of control animals through exposure to an infected guinea pig. Two naïve contact animals were inoculated intranasally with Pan/99 virus. At 24 h postinoculation, two control guinea pigs with no previous exposure were each placed into the same cage with one infected animal. (H) Results of control challenge through contact with an infected guinea pig. Intranasally infected contact animals shed high titers of virus into nasal washes (white squares with dashed lines), and control guinea pigs with no previous exposure to Pan/99 virus (black triangles with solid lines) became infected through contact with the infected animals.