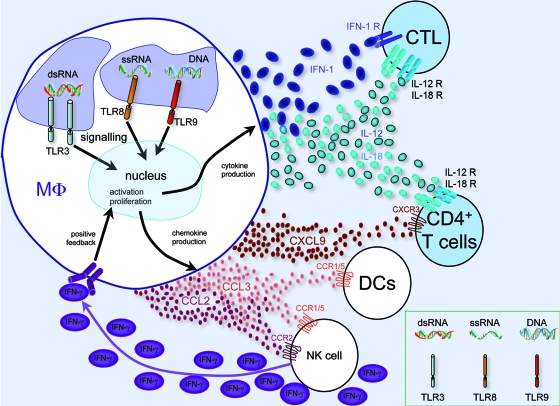
FIG. 1.
Macrophages in viral infection. Phagocytosed viral DNA and/or RNA is recognized by the endosomal TLRs TLR3 (dsRNA), TLR8 (single-stranded RNA [ssRNA]), and TLR9 (DNA), which lead to signaling, transcriptional changes, and macrophage activation and proliferation, as well as to antigen presentation (not shown). As a result, cytokines (IFN-1, IL-12, and IL-18) and chemokines (CCL2, CCL3, and CXCL9) are produced, recruiting further immune cells of the innate and adaptive immune systems (NK cells, DCs, and T cells). Positive feedback via NK cell-produced IFN-γ (purple ovals) leads to further macrophage activation. The macrophage-produced cytokines type I IFN (IFN-α and IFN-β), IL-12, and IL-18 stimulate a type 1 immune response in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Recruited DCs present viral antigens, including activated CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, to T cells, destroying infected cells (not shown). MΦ, macrophage.