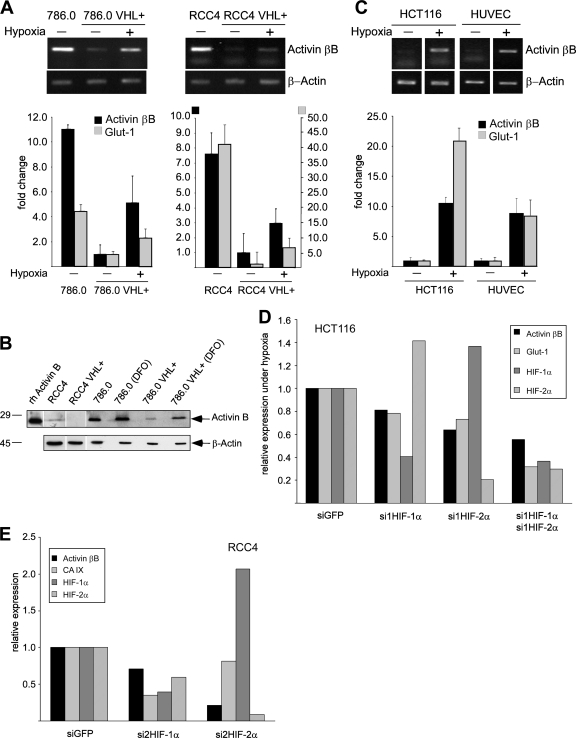
FIG. 1.
Activin B expression is downregulated by VHL and upregulated by hypoxia. (A) Qualitative (upper panels) and quantitative (bar graph; n = 3) RT-PCR analysis for activin βB mRNA in VHL-deficient 786.0 and RCC4 parental cell lines and stable transfectants expressing wild-type VHL (VHL+) kept under normoxia (−) or hypoxia (+) for 16 h. The HIF target Glut-1 was analyzed as a positive control. (B) Western blot detection of activin B in cell supernatants collected from indicated cell lines and of recombinant human activin B (rh Activin B). Western blotting of β-actin from cell extracts of the same cultures was used to control for similar cell numbers. DFO, treatment with DFO for 16 h. (C) Qualitative (upper panels) and quantitative (bar graph; n = 3) RT-PCR analysis for the activin βB mRNA from HCT116 colon cancer cells and HUVEC kept under normoxia (−) or hypoxia (+) for 16 h. The HIF target Glut-1 was analyzed as a positive control. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for the activin βB, Glut-1, HIF-1α, and HIF-2α mRNAs in HCT116 cells transfected with siGFP (as a negative control) or siRNAs against HIF-1α (si1HIF-1α) and/or HIF-2α (si1HIF-2α). Cells were kept under hypoxia for 16 h after siRNA transfection. Results were normalized to the expression of β-actin and siGFP. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis for the activin βB, CA IX, HIF-1α, and HIF-2α mRNAs in RCC4 cells transfected with siGFP (as a negative control) and siRNAs against HIF-1α and HIF-2α. Results were normalized to the expression of β-actin and siGFP. Note that siRNA against HIF-2α was more efficient than siRNA against HIF-1α. Similar results were obtained with a second, unrelated set of siRNAs to HIF-1α and HIF-2α.