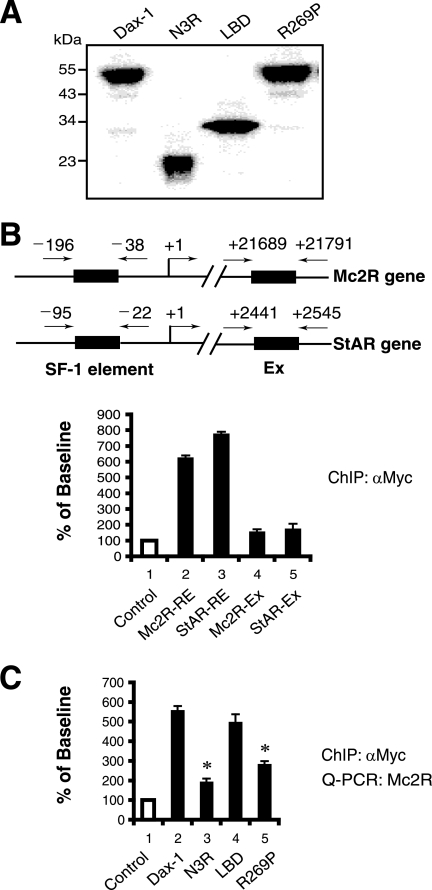
FIG. 6.
Dax-1 is recruited to SF-1 target promoters, but the Dax-1 mutants N3R and R269P exhibit decreased promoter occupancy. (A) Expression of Dax-1-Myc and its mutant versions. Y1 cells were transfected with equal amounts of vectors expressing Myc-tagged wild-type Dax-1 and its mutant forms N3R, LBD, and R269P. The cells were lysed 48 h later and subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-Myc antibody. (B) Dax-1-Myc is recruited to the Mc2R and StAR promoters. ChIP assays of transiently expressed Dax-1-Myc in Y1 cells were performed using anti-Myc antibody (αMyc). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by real-time PCR using primers designed against the SF-1 response elements (RE) in the proximal Mc2R and StAR promoters. Data are normalized to the value obtained using normal IgG as a negative control for immunoprecipitation, set at a baseline of 100. Bars 4 and 5 show the results obtained using PCR primers directed against downstream exons (Ex) to which Dax-1 would not be expected to bind. Experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated three times. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Myc-tagged Dax-1 mutants N3R and R269P are defective in recruitment to the Mc2R promoter. Similar to the experiments described in the legend to panel B, ChIP assays were conducted with transiently expressed Dax-1-Myc wild-type or mutant proteins as indicated (*, P < 0.0001 for bars 3 and 5 versus bar 2 [the P value for bar 4 versus bar 2 was not significant] by ANOVA followed by Scheffe's test). Q-PCR, quantitative PCR.