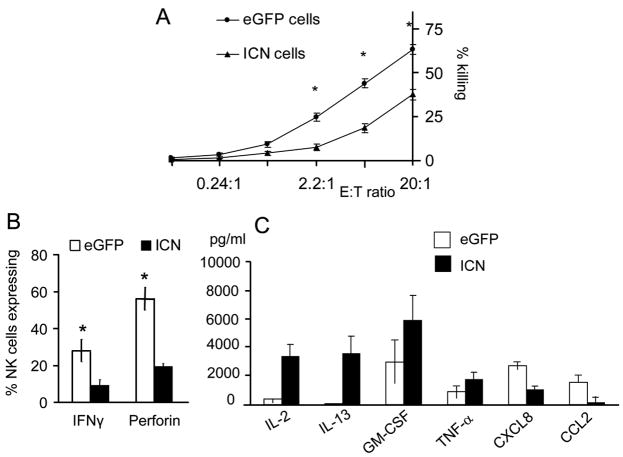
Figure 4. CD34+ICN+ derived NK cells are hyporesponsive and exhibit immature function.
(A) ICN+ and eGFP+ derived cells were cultured with EL08-1D2 stroma and cytokines (Flt3-L, IL-7, c-kit-L, IL-15, IL-3). Stroma cultured CD34+ derived cells were harvested at day 28 and compared in 51Cr release cytotoxicity assay against K562 targets at various E:T ratio as shown. ICN+ derived cells (▲) showed a significant reduction in cytotoxicity compared to eGFP+ cells ( ) (mean of 7 independent experiment ± SEM shown; *P< .05). (B) Cultured CD34+ICN+ and CD34+eGFP+ cells were harvested at day 28 and suspended in concentration 1×106 cells/mL. Interferon-γ production was analyzed by intracellular stain following stimulation with IL-12 (10 ng/mL) and IL-18 (100 ng/mL) for 18 hours, followed by Brefeldin A in the last 5 hours of the incubation and permeabilization using cytofix/cytoperm (4 independent experiments ± SEM; *P< .05). (C) Chemokines and cytokines were measured by Luminex from eGFP+ and ICN+ cell free supernatants prepared after stimulation of 106 cells/well with PMA/ionomycin. Significant differences between eGFP+ (□) and ICN+ (■) cell-free supernatants were seen for IL-13, GM-CSF, and CCL2 (MCP-1) and IL-2 (mean of 5 independent experiments with SEM is shown; *P< .05).
) (mean of 7 independent experiment ± SEM shown; *P< .05). (B) Cultured CD34+ICN+ and CD34+eGFP+ cells were harvested at day 28 and suspended in concentration 1×106 cells/mL. Interferon-γ production was analyzed by intracellular stain following stimulation with IL-12 (10 ng/mL) and IL-18 (100 ng/mL) for 18 hours, followed by Brefeldin A in the last 5 hours of the incubation and permeabilization using cytofix/cytoperm (4 independent experiments ± SEM; *P< .05). (C) Chemokines and cytokines were measured by Luminex from eGFP+ and ICN+ cell free supernatants prepared after stimulation of 106 cells/well with PMA/ionomycin. Significant differences between eGFP+ (□) and ICN+ (■) cell-free supernatants were seen for IL-13, GM-CSF, and CCL2 (MCP-1) and IL-2 (mean of 5 independent experiments with SEM is shown; *P< .05).