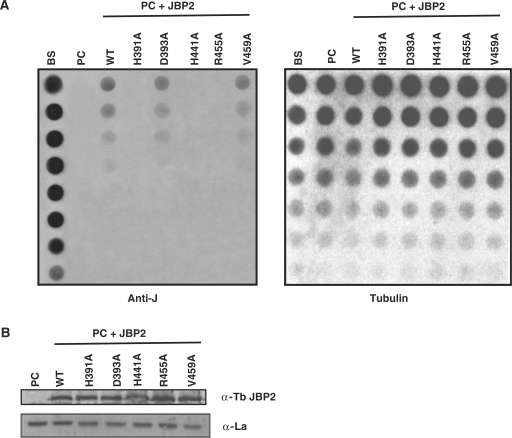
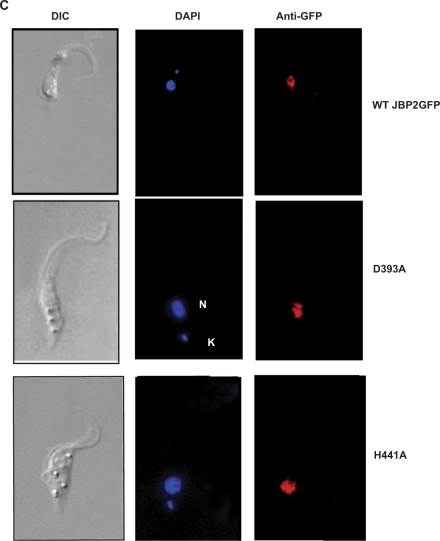
Figure 2.
Conserved residues with in the TH domain of JBP2 are critical for the protein to stimulate de novo J synthesis. (A) Dot-blot analysis of the JBP2 TH mutants. DNA was isolated from procyclic (insect stage) cells expressing either WT or mutant JBP2 and analyzed for J content by spotting DNA diluted onto a membrane and incubated with anti-J antisera. BS, WT bloodstream form cells; PC, WT procyclic cells; PC+JBP2, procyclic cells expressing JBP2 GFP; WT, procyclic cells expressing WT JBP2. H391A, D393A, H441A, R445A are procyclic cells expressing mutant versions of JBP2 as indicated in Figure 1. V459A is a control substitution of a residue outside the catalytic domain. (B) Expression of WT and mutant JBP2 in insect stage cells. Procyclic trypanosomes expressing either WT or mutant JBP2 were analyzed by western blot using anti-JBP2 antisera. Anti-La antisera was used as a loading control. Extract from untransfected procyclic cells is included as a negative control. (C) JBP2-GFP expression in procyclic trypanosomes was visualized microscopically by anti-GFP staining on formaldehyde fixed cells. DAPI staining reveals the localization of the nucleus (N) and the kinetoplast (K). WT JBP2, procyclic cells expressing WT protein; D391A, H441A are the corresponding mutant JBP2-GFP proteins.