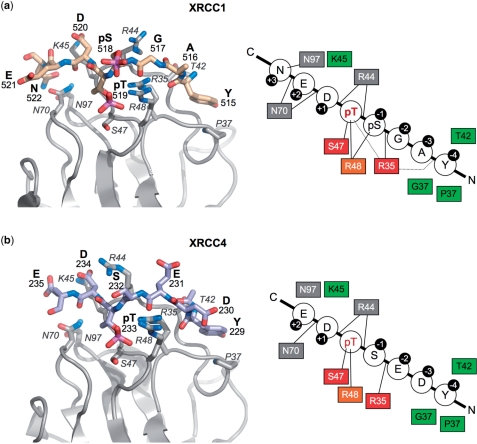
Figure 4.
Comparison of PNK–FHA interactions with XRCC1 and XRCC4. PNK–FHA interacts in a similar way with the XRCC1 phosphopeptide (a), as with the XRCC4 peptide (b) apart from the additional interactions with pSer518 and Asn522 in the XRCC1 complex. That Ser518 was not phosphorylated in the XRCC4 complex is probably responsible for the different conformation observed for Arg44 in the two complexes. In both cases, the residues at −2 and −3 relative to the pThr, make no side-chain contacts with the protein that could mediate selectivity for these positions, and the specificity of FHA for the XRCC1 and XRCC4 sequences resides in the polar and electrostatic interactions with phosphorylated and acidic residues at 0, −1, +1 and +2, the hydrophobic interaction with Tyr at −4, and (for XRCC1) with the amide-side chain of the Asn at +3. In the schematics on the right, residues with a red (strictly) or orange (highly) background are conserved across FHA domains. Those with a green background are involved in hydrophobic contacts with the bound XRCC1/XRCC4 peptide, whilst those with a grey background are involved in making specific hydrogen bonds (as indicated by a line).