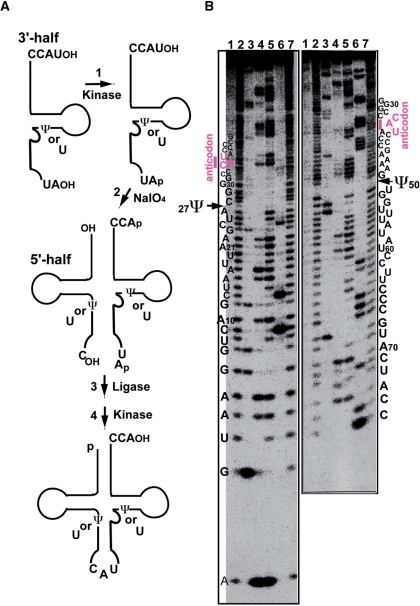
Figure 3.
Preparation of synthetic tRNAMet variants. (A) Process of synthesizing mt tRNAMet by a combination of chemical synthesis and ligation (33). The synthetic tRNAs have sequences identical to the respective sequences of native tRNAMet, except for f5C and pseudouridine (Ψ). (B) Sequencing analysis using the Donis–Keller′s method of the synthetic mt tRNAMet labeled with [32P] at the 5′-end (left) and the 3′-end (right), respectively (30,32). Electrophoresis was performed on a 15% polyacrylamide–7 M urea–10% glycerol gel. Lanes: control without ribonuclease (RNase) (lane 1); limited alkaline hydrolysis (lanes 2 and 7); digestion by RNase T1 (specific for G: lane 3), RNase U2 (specific for A: lane 4), RNase PhyM (specific for A and U: lane 5) and RNase CL3 (specific for C: lane 6). As indicated by the arrows, Ψ was not digested by RNase PhyM (12). The numbering of the residues in the cloverleaf structure of the mt tRNA conforms to that in the previous report (71).