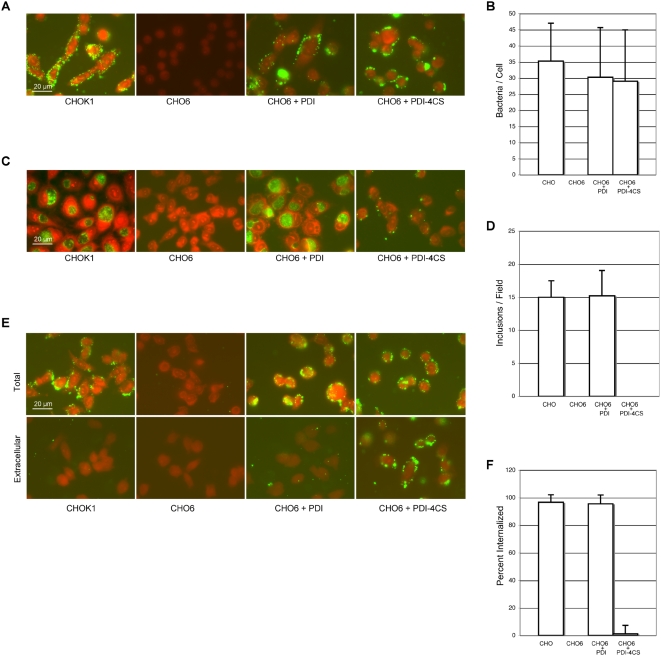
Figure 3. PDI enzymatic activity is necessary for bacterial entry but not for attachment.
CHO6 cells were transfected with vectors expressing wildtype PDI (CHO6+PDI) or an enzymatic mutant of PDI lacking active site cysteine residues (CHO6+PDI-4CS). 48 h after transfection, cells were infected with Chlamydia for subsequent attachment and entry analysis. Cells were fixed and evaluated by immunofluorescence, bacteria are green and counter staining shown with Evans blue. (A) Bacterial attachment was analyzed 1 h post-infection. Bacterial attachment was recovered in CHO6+PDI as well as in CHO6+PDI-4CS, indicating that PDI enzymatic activity is not necessary for bacterial attachment. (B) The number of bacteria attached to cells was determined by quantification, the number of bacteria associated with each cell in eight separate fields of view containing at least ten cells. Error bars indicate standard of deviation (STDEV). (C) 24 h after infection Chlamydia infectivity was evaluated. Infectivity was restored in CHO6+PDI. No productive infection was observed in CHO6 cells or in CHO6+PDI-4CS. In CHO6+PDI-4CS, the bacteria remained persistently attached to the cell, indicative of the requirement for PDI enzymatic activity for bacterial entry. (D) Infection was quantified by counting the number of inclusions per field of view in eight separate fields of view containing at least ten cells. Error bars indicate the STDEV. (E) Cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 h to allow for bacterial entry. Entry was analyzed by comparing the total number of cell-associated bacteria for staining of permeabilized cells (Total) and the number of extracellular bacteria determined by staining unpermeabilized cells (Extracellular). Bacterial entry was recovered in CHO6 cells expressing PDI (CHO6+PDI) but not in CHO6 cells expressing enzymatically nonfunctional PDI (CHO6+PDI-4CS). (F) Percent internalization represents 1 minus the number of extracellular bacteria divided by the total number of bacteria multiplied by 100. The number of extracellular and total bacteria was determined by quantifying the number of bacteria associated with each cell per field of view in eight separate fields of view containing at least ten cells. Error bars indicate the STDEV.