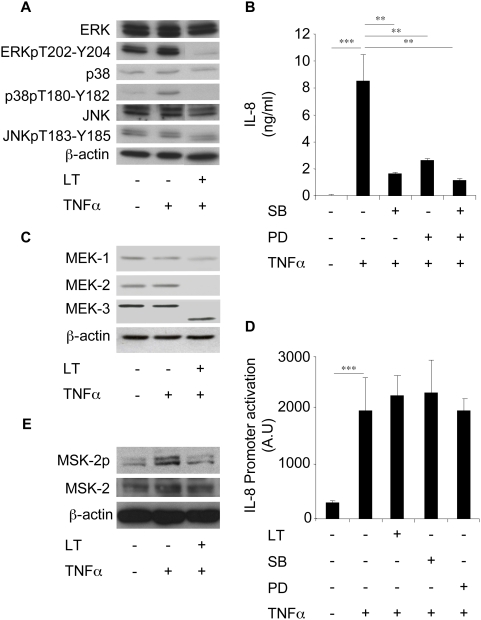
Figure 4. LT inhibits IL-8 expression via a MAPK-dependent pathway in Beas-2B cells.
(A) Beas-2B cells were incubated for 1 h with LT (1 µg/ml) and stimulated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for an additional 2 h. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies directed against ERK, phospho-ERK (ERKpT202-Y204), p38, phospho-p38 (p38pT180-Y182), JNK, and phospho-JNK (JNKpT183-Y185) and were normalized with ß-actin antibody. (B) Cells were pretreated with SB203580 (10 µM) or PD98059 (10 µM) for 1 h before incubation with TNFα (10 ng/ml). IL-8 concentrations were measured in supernatants after 24 h stimulation. (C) Cells were incubated for 1 h with LT (1 µg/ml) and stimulated by TNFα (10 ng/ml) for an additional 2 h. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies directed against MEK-1, MEK-2, and MEK-3 and were normalized with ß-actin antibody. (D) Cells were transfected with an IL-8 promoter reporter plasmid, and then incubated for 1 h with LT (1 µg/ml), SB203580 (10 µM), or PD98059 (10 µM) before addition of TNFα (10 ng/ml). Luciferase activity was then measured after 24 h stimulation. (E) Cells were incubated for 1 h with LT (1 µg/ml) and stimulated by TNFα (10 ng/ml) for an additional 45 min. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies directed against MSK-2 and phospho-MSK-2 and normalized with ß-actin antibody.