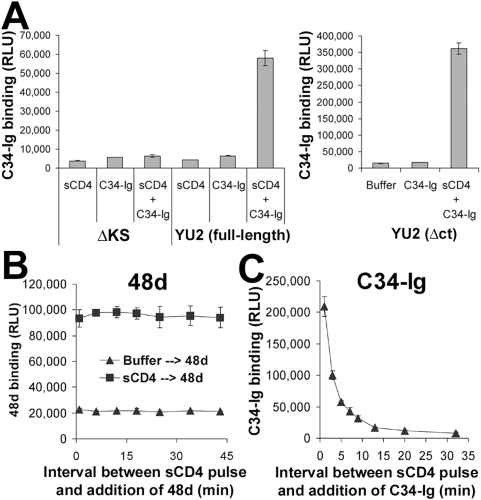
Figure 2. Soluble CD4-induced changes in the gp120 coreceptor–binding region and gp41 HR1 region.
(A) A cell-based ELISA was used to measure the binding of C34-Ig, which detects the HR1 gp41 region [38],[47], to the trimeric HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins. COS-1 cells were transfected with the negative control ΔKS plasmid or plasmids expressing the full-length YU2 envelope glycoproteins (left) or the cytoplasmic tail-deleted (Δct) YU2 envelope glycoproteins (right). Two days later, cells were incubated with C34-Ig (20 µg/ml), in the presence or absence of sCD4 (20 µg/ml). C34-Ig binding was measured using a secondary horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody. (B,C) Change over time in the exposure of CD4-induced epitopes. Cells that express the YU2(Δct) envelope glycoproteins were pulsed for three minutes with sCD4 (40 µg/ml). Cells were then washed three times and incubated for different time periods at 37°C. The monoclonal antibody 48d (B) or C34-Ig (C) was then added. The bound 48d or C34-Ig molecules were detected using a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-human IgG Fc antibody, as described in Materials and Methods. Values represent the mean RLU (±s.e.m.) of two replicate samples.