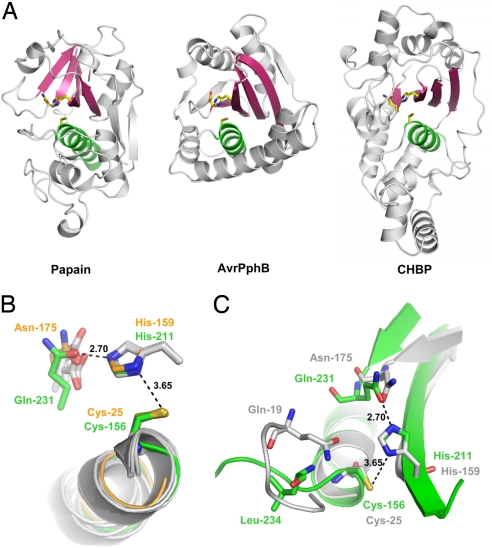
Fig. 3.
CHBP adopts a papain-like fold and shares a catalytic triad. (A) Structure comparison of CHBP with papain-like enzymes. (Left) Papain (PDB ID code 1PPN). (Center) AvrPphB (PDB ID code 1UKF). (Right) CHBP. Relative orientation of the structures is based on least-squares superimposition of the catalytic Cys and His residues. The catalytic triad residues are shown as sticks. The conserved core helix and β-sheets are colored green and pink, respectively. (B) Comparison of the active sites of CHBP and papain-like enzymes. The superimposition was based on Cys-156 and His-211 in CHBP and the corresponding residues in papain (Cys-25 and His-159) and four other papain family members (PDB ID codes 1UKF, 1XD3, 1EVU, and 2BSZ). Active-site residues of CHBP and papain are shown as stick models in green and orange, respectively; active-site residues in the other four papain family members are shown as gray stick models. (C) Potential oxyanion hole in CHBP. The catalytic triad of CHBP shown in green is superimposed onto that of papain (gray). The associated secondary structures are colored accordingly. Upon superimposition, the main-chain amide of Leu-234 in CHBP is closest to the side-chain amide of Gln-19 in papain that forms an oxyanion hole with the backbone amide of Cys-25.