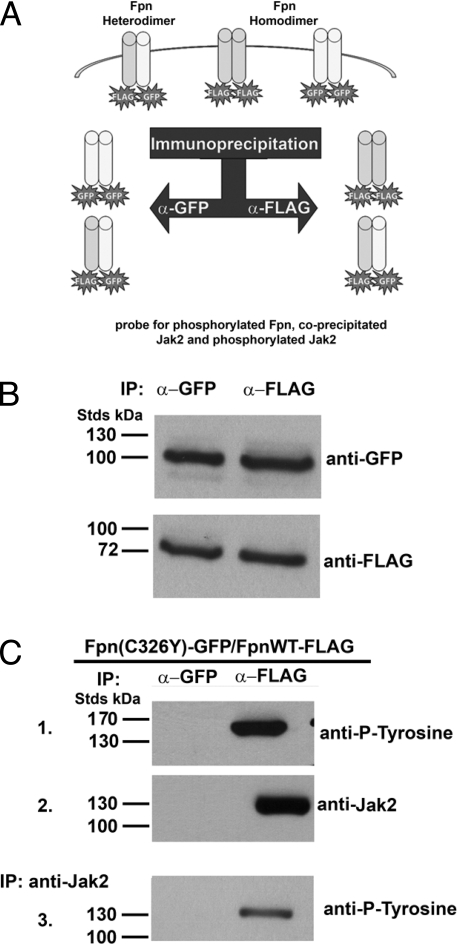
Fig. 5.
Two hepcidin binding sites on the Fpn dimer are required for Jak2 binding. (A) Schematic of experimental design. Cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Fpn-FLAG and mutant Fpn-GFP. Cells were incubated in the presence or absence of hepcidin and then immunoprecipitate with either anti-FLAG or anti-GFP antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were then analyzed for Fpn, phospho-Fpn, Jak2, and phospho-Jak2. (B) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids containing WT Fpn-FLAG and Fpn(C326Y)-GFP. Cells were incubated in the presence of 1 μg/ml hepcidin for 30 min, solubilized, and immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-GFP or anti-FLAG antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot using anti-FLAG or anti-GFP antibodies. (C) Immunoprecipitated samples were analyzed by Western blot using mouse anti-phosphotyrosine (1) or rabbit anti-Jak2 followed by a peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse or goat anti-rabbit IgG (2). A second immunoprecipitation was performed with rabbit anti-Jak2 and the immunoprecipitation samples were analyzed by Western blot using mouse anti-phosphotyrosine followed by a peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (3).