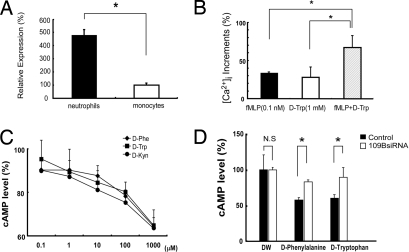
Fig. 4.
(A) Expression of GPR109B in human neutrophils. Expression of GPR109B mRNA in human neutrophils is determined by real-time RT-PCR analysis, and the relative expression level is expressed as percentage of that in human monocytes. Data represent mean value ± SEM (n = 4). *, P < 0.05 vs. monocytes. (B) D-Trp enhanced intracellular calcium mobilization induced by fMLP at a low dose in human neutrophils. Neutrophils were loaded with 10 μM Fura-2AM for 2 h at room temperature, and intracellular calcium mobilization was measured. All values are expressed as a percentage of control (fMLP, 100 nM). Data represent mean value ± SEM (n = 4). *, P < 0.05 vs. fMLP (0.1 nM) or D-Trp (1 mM). (C) D-Phe, D-Trp, and D-Kyn inhibit cAMP production in neutrophils through GPR109B. Neutrophils were incubated with D-amino acids together with 50 μM forskolin. After 15 min, cAMP accumulation was measured. cAMP content is expressed as a percentage of control in the absence of D-amino acids. Data are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. (D) Effects of GPR109B knockdown on D-amino acids-induced decrease in cAMP level in human neutrophils. Transfection with GPR109B siRNA significantly inhibited the decrease of cAMP level by D-Phe and D-Trp in neutrophils as compared with control siRNA.