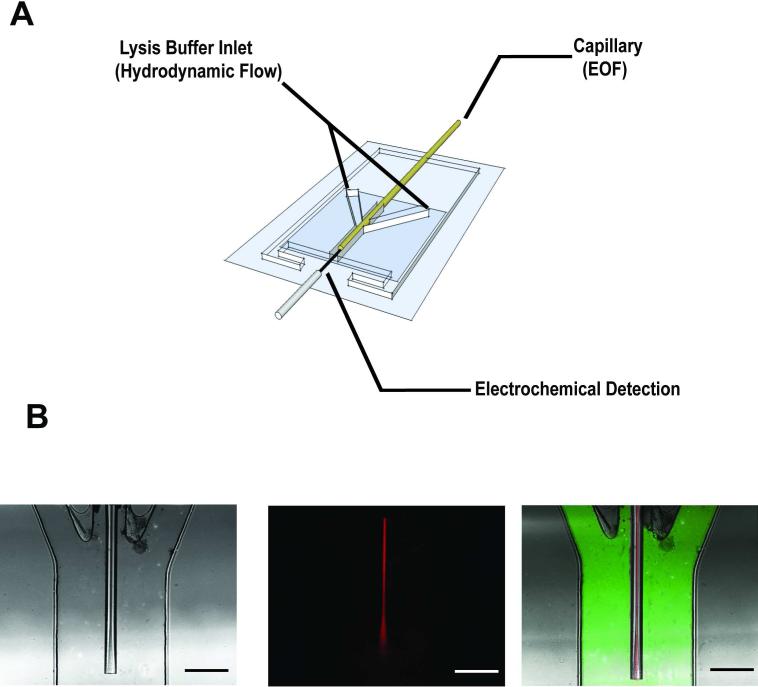
Figure 1.
Three layer PDMS device for the end-column lysis and electrochemical detection of vesicles separated by capillary electrophoresis. (A) Schematic of device (not drawn to scale). Three 200 μm × 125 μm channels converge into a 650 μm × 125 μm channel where contents exiting the capillary are lysed and detected at a carbon-fiber microelectrode. (B) Bright field and confocal fluorescence images of the device. A continuous injection 100 μM rhodamine B solution (red) is flowed through the capillary using electroosmotic flow (166 V/cm) and 36 μM FITC solution (green) is flowed through the lysis channels using hydrodynamic flow controlled by a syringe pump (0.5 μ/min, scale bar = 200 μm).