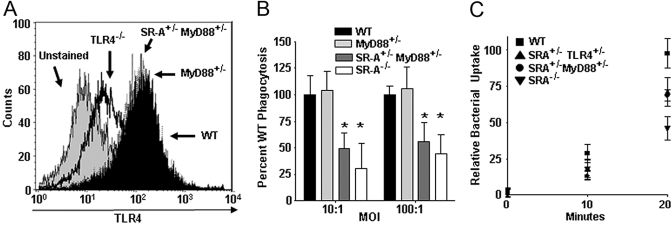
Fig. 5.
SR-A+/−TLR4+/− BMDC exhibit impaired kinetics of bacterial internalization and SR-A+/−MyD88+/− cells recapitulate this defect. (A) FACS histogram showing TLR4 cell-surface expression on BMDC from WT, TLR4−/−, MyD88+/−, and SR-A+/−MyD88+/− mice. MyD88 heterozygosity does not affect cell-surface expression of TLR4. (B) Gentamycin protection assays were performed on WT, MyD88+/−, SR-A+/−MyD88+/−, and SR-A−/− BMDC using E. coli bacteria. SR-A+/−MyD88+/− and SR-A−/− BMDC showed significant impairment in phagocytosis of E. coli (*, P<0.05) compared with WT cells. For all graphs, n ≥ 18 for all genotypes, and the means and sd are shown. (C) Kinetic analysis of bacterial uptake was performed on WT, SR-A+/−TLR4+/−, SR-A+/−MyD88+/−, and SR-A−/− BMDC. Quantitative uptake of bacteria by BMDC was assessed every 10 min using a gentamycin protection assay to determine the relative rates of phagocytosis for the indicated BMDC genotypes. SR-A+/−TLR4+/−, SR-A+/−MyD88+/−, and SR-A−/− BMDC show impairment for the internalization of bacteria as early as 10 min after BMDC-bacteria coincubation, and this deficit is fully apparent by 20 min after bacterial exposure. For all graphs, the means and sd are shown.